MF3d
Investment Thesis
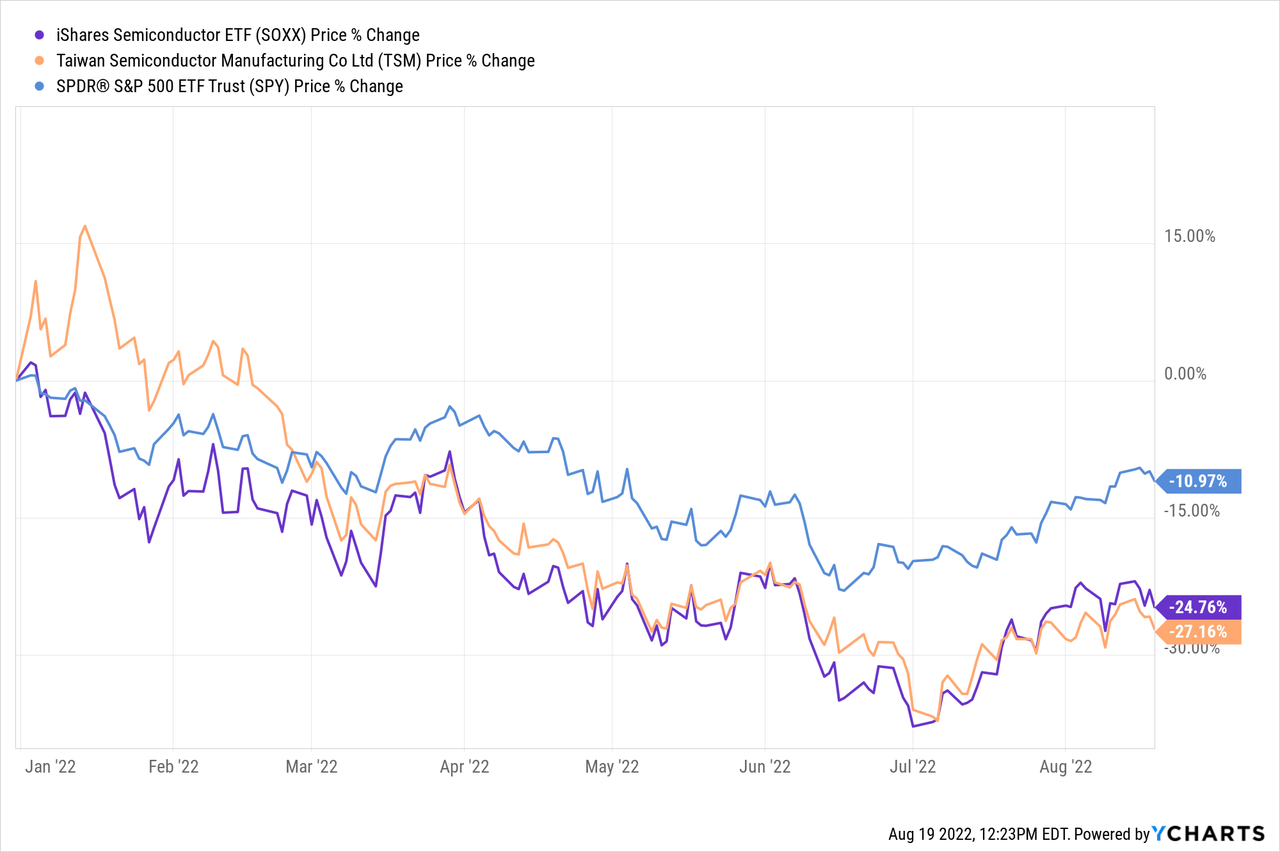
Undoubtedly, it might not be the best time to own semiconductor stocks due to the macroeconomic and sector headwinds. However, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited (NYSE:TSM), which is down around 27% YTD, remains the undisputed leader in the semiconductor space, expanding its competitive advantage and economic moat, which supports my bullish thesis on TSM.
Flexing A Competitive Edge Over Peers
Global foundry output is dominated by Taiwan, capturing more than 60% of the total production. TSMC alone has a 54% market share and is a world leader in the foundry business. The company is one of only three companies worldwide, along with Intel Corporation (INTC) and Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (OTCPK:SSNLF), capable of producing sub-10nm semiconductors. Big tech companies like Apple Inc. (AAPL), MediaTek, Nvidia, Qualcomm (QCOM), and many other fabless companies depend on the foundry services of TSMC.
Not surprisingly, TSMC leads all competitors in wafer processes and advanced packaging technologies. The company’s success can be attributed to its foundry business model. Moreover, the economies of scale in a capital-intensive business like foundries favor the largest players. Thus, TSMC’s foundry business will further strengthen in the following years as its peers face a minimal competitive challenge. TSMC intends to spend aggressively on R&D and capacity, as the company plans to spend approximately $40 billion this year in capital expenditure, keeping in view its massive new fab construction plans.
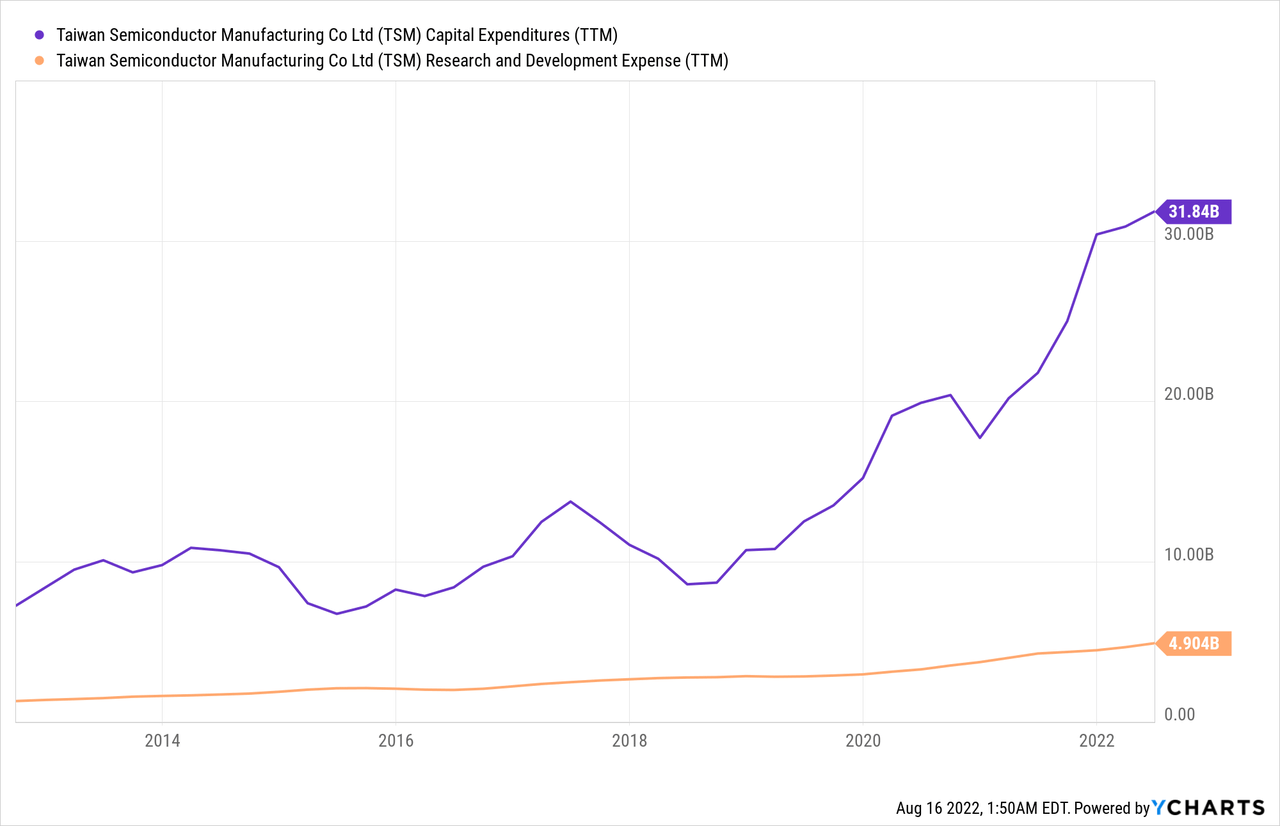
As the world enters a new era of superpower competition, TSMC will need to reduce the concentration of its manufacturing operation in Taiwan by building facilities outside the country and the region. TSMC is currently spending $12 billion on building a plant in Arizona that is expected to begin production in 2024 and marks TSMC’s first U.S.-based plant in 20 years. As a result, TSMC is now firmly positioned as the key enabler of the new computing revolution in the semiconductor industry, with multiple architectures, chip platforms, and design teams competing to push computing and AI innovation.
The Growth Catalysts: HPC and 5G
The semiconductor industry is expected to grow by 9% YoY in 2022. However, some of the company’s clients face inventory adjustments due to the lackluster demand for consumer electronics. An inventory adjustment happens in the semiconductor space if demand declines for a prolonged period during both economic expansion and contraction and often lasts two to three quarters.
Nevertheless, the company raised its 2022 revenue YoY growth guidance to mid-30%, given growth momentum coming from High-performing Computers (HPC), IoT/5G, and the steady demand for automotive and datacenter. Additionally, revenue contribution from the 5nm is expected to increase in the foreseeable future, but HPC remains the main growth driver in the long run.
Growth Drivers QoQ (investor.tsmc.com)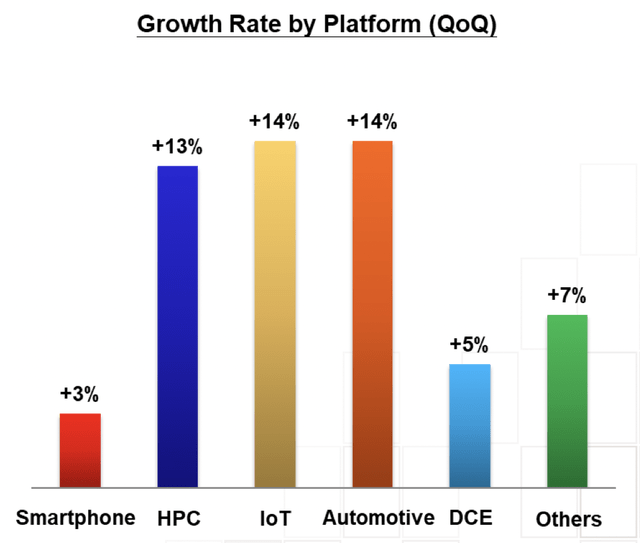
Moreover, TSMC forecasts that the penetration rate of 5G handsets may reach 50% in 2022, persistently catalyzed by 5G development. Despite the decelerating growth in the handset sector, the trend of higher penetration of 5G handsets may remain unchanged. Many chips in 5G handsets are made via TSMC’s advanced processes, such as built-in multiple camera modules, RF, AP, modem chip, and PMIC.
5G Penetration Rate (eetasia.com)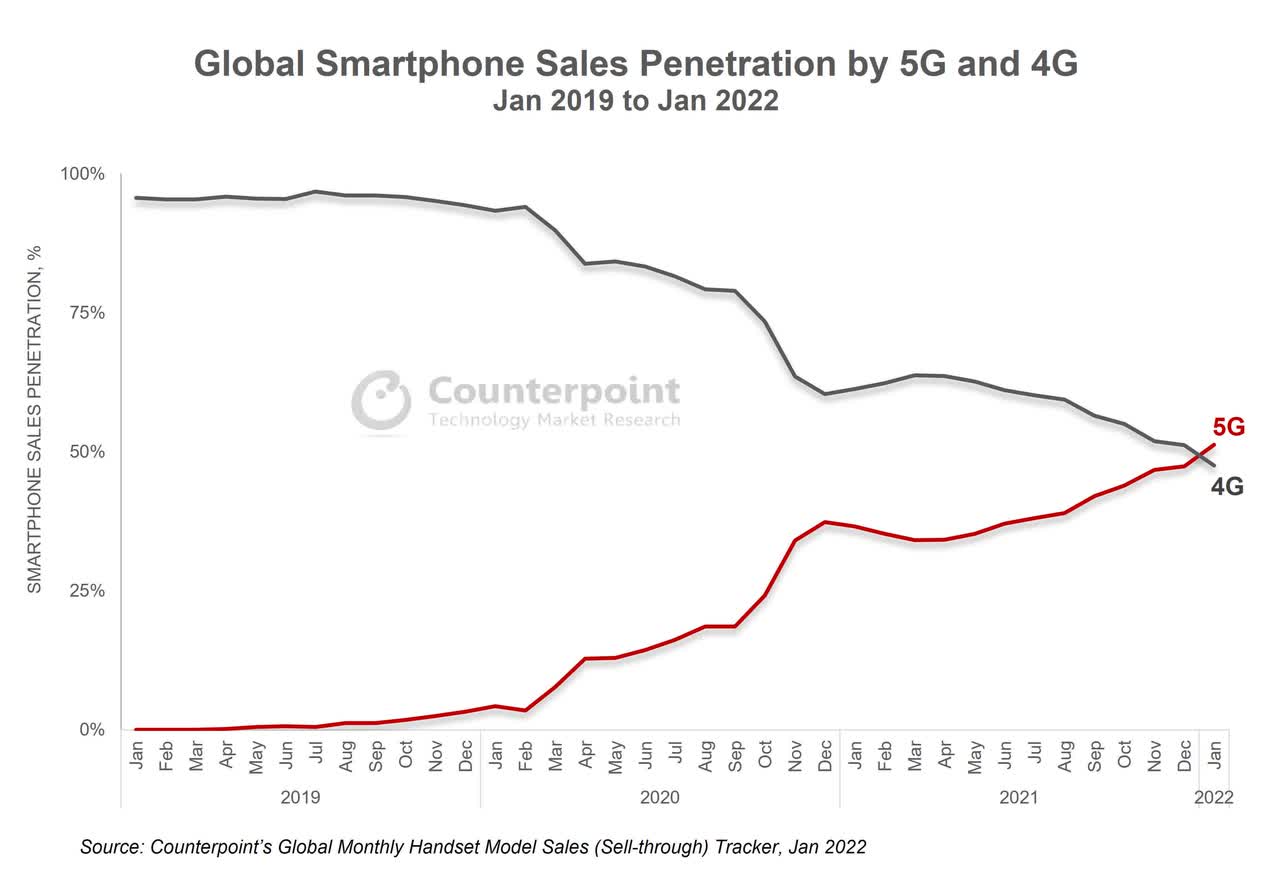
A Cyclical Downturn Is Manageable
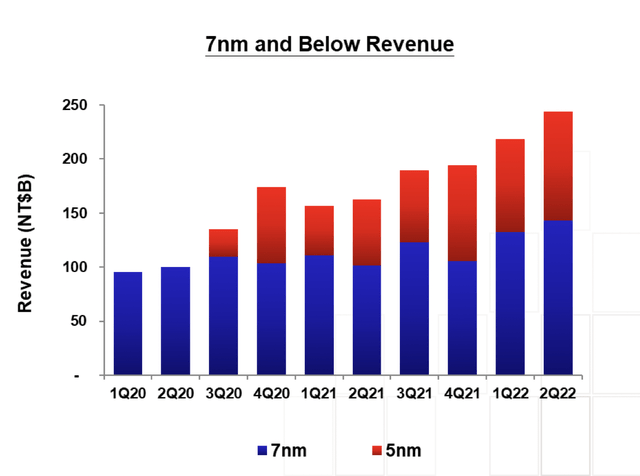
The current inventory adjustment in the semiconductor industry may take a few quarters, and it may last until 1H23 before inventory returns to a healthy level. Older process technologies should see some utilization pressure in 2023, given the prospects of an inventory correction and cyclical downturn. Still, the impact is likely to be manageable, as the mix of revenues for the company is now overwhelming leading-edge, with almost two-thirds of revenues expected to derive from 7nm and below by 2023. On the contrary, the demand related to automotive and datacenter will remain intact.
Taking The Lead In Advanced-Node Chip
TSMC’s market dominance in advanced-node chip manufacturing (10nm or smaller) will persist at least in the medium term despite ongoing challenges from Intel and Samsung. TSMC has demonstrated mastery in cutting-edge technology, and the stage is set for a smooth transition to 3-nm node manufacturing, as scheduled in 2H22. TSMC is moving from strength to strength while its peers lag, as Intel is not having the technology yet to produce 5-nm and lower chips, and Samsung is still struggling to improve the production yield of 4-nm nodes, a previous generation.
As a result, TSMC is poised to control over half of the world’s advanced-node chip manufacturing capacity over the next three years. In addition, the management has stated that the company will have EUV lithography machines by 2024 (faster than Intel), which would further catalyze the dominance of TSMCs in advanced-node chips.
Strong N3 Pipeline
The 3nm chip or “N3” is a big deal for the tech industry as this chipset development method is expected to offer up to 15% speed improvement, 30% power consumption reduction, and 70% logic density gain. In addition, TSMC confirmed a strong N3 pipeline for both smartphone and HPC customers. Thus, TSMC should boost a near-100% share in N3 in the medium term, with QCOM, NVDA, Intel, AMD, and Mediatek all reliant on TSMC.
The growth prospects for N3 will stay strong in the next few years, underpinned by a strong N3 design pipeline and tape-out activities. Apple has been the primary customer for TSMC’s leading-edge nodes and will remain the key customer for N3 in the next few years. In addition, Apple will migrate its iPhone processors (A17) to N3 in 2H23 for Pro/Pro Max models.
QCOM has returned to TSMC for its flagship 5G SoC (Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 plus) from 2H22, based on TSMC N4. In addition, QCOM has been engaging with TSMC for future SoC development due to stronger transistor performance, better power consumption, and higher yields than Samsung Foundry. Furthermore, NVIDIA Corporation (NVDA) will move its wafer production for next-generation gaming GPU (RTX40 series, Ada Lovelace architecture) to TSMC N5 from 2H22.
TSMC Technology Roadmap 2022 (semiwiki.com)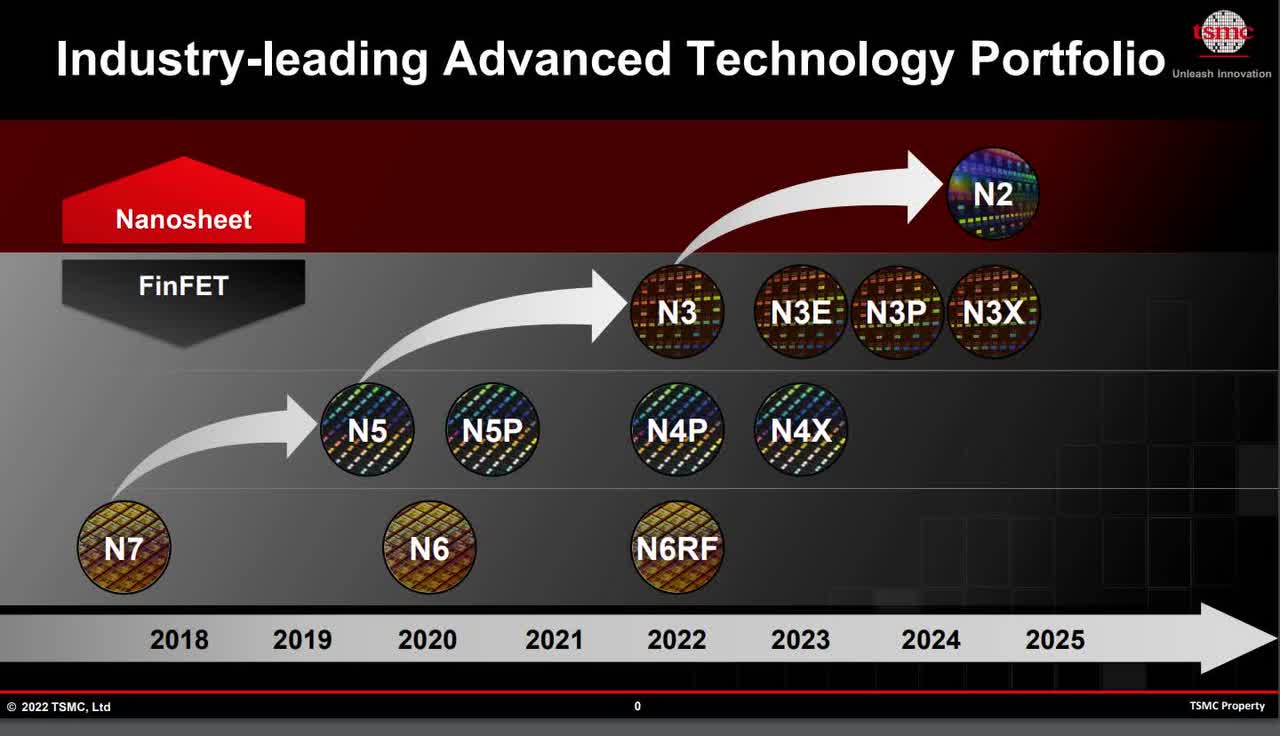
The CHIPS & Science Act
Taiwan accounts for over 90% of the world’s most advanced chips used for military defense and corporate computing services, with TSMC the dominant producer. In addition, Apple, MediaTek, and Qualcomm, which control over 85% of the handset chip market, rely on TSMC’s supply. Moreover, the CHIPS and Science Act in the US will provide over $50 billion of subsidies to promote domestic semiconductor production and research. Still, the immediate impact will be small as it would take years for new capacity to unfold. As a result, Taiwan will remain the largest producer of chips, particularly with advanced nodes, at least in the medium term.
Taiwan-China Escalating Tensions
According to analysts, Taiwan’s dominance in manufacturing semiconductors could prove crucial in deterring an invasion by Beijing. Beijing relies heavily on Taiwanese technology to power key industries it is banking on to double its GDP by 2035. Taiwan accounts for 92% of global production for semiconductor process nodes below 10nm, making it the leading supplier of the vast majority of chips that power the world’s most advanced machines, from Apple iPhones to F-35 fighter jets.
According to Ray Yang, consulting director at Taiwan’s Industrial Technology Research Institute:
China is good at algorithms, software, and market solutions, But their industry needs many high-performance computer (HPC) chips that they do not have. If a conflict interrupted their supply, it would dramatically slow down China’s AI and 6G ambitions. They would have to reorder their entire industrial strategy.
Not surprisingly, according to a Boston Consulting Group analysis, a one-year interruption in the supply of Taiwanese chips alone would cost global tech companies around $600 billion. Last but not least, Pelosi’s visit to Taiwan further escalated China’s rage over Taiwan, entering a “very dangerous” phase, as Ray Dalio noted. However, it remains to be seen how the geopolitical arena will unfold.
Concluding Thoughts
Inventory correction and macro uncertainty may raise concerns about a cyclical bottom for semiconductors. Still, TSMC’s sustainable positive free operating cash-flow generation and solid net cash may enable the chipmaker to weather operating volatility amid strong demand for 5G high-performance computing and AI.
Moreover, its strengthening technological capabilities, particularly in the most advanced nodes, and profit margin that roundly beats peers may help it fend off competition and protect its dominance in the sector. CAPEX may remain high on rapid technological changes in the sector and geographic diversification from Taiwan, but its profit generation should sufficiently meet that amid a prudent shareholder return policy.
Despite the inventory adjustment and unfavorable macroeconomic environment, TSM is well positioned to grow and beat expectations, making it a strong buy at current levels.


Be the first to comment