FinkAvenue
Company overview
Macy’s (NYSE:M) is a chain of high-end department stores in the United States: it operates 725 stores across 43 states and generates $25 bn in revenues.
- Most stores are located at urban or suburban sites, principally in densely populated areas across the United States.
- The Company and its predecessors have been operating department stores since 1830.
- It focuses on a wide spectrum of apparel, including women’s, men’s, sport, fragrances, jewelry and watches, household items and much more.
- Headquartered in New York City, USA, the company comprises three retail brands: Macy’s, Bloomingdale’s and Bluemercury.
Exhibit 1: iconic brands
Source: annual report
For now, Macy’s competes with several large department store chains, namely Kohl’s (KSS), Nordstrom (JWN) and Dillard’s (DDS).
Despite being the leader in the department stores segment, Macy’s has been suffering similar problems to those of other department stores: diminishing traffic and falling margins, which have continued for several years now.
Exhibit 2: top shareholders
Top shareholders (Bloomberg, Analyst research)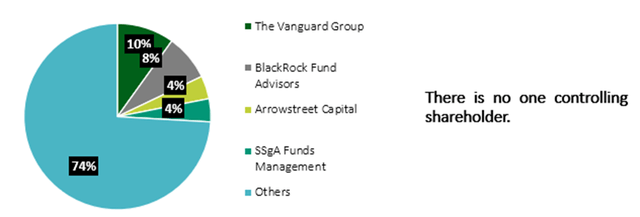
Source: Bloomberg, Analyst research
Financials
Macy’s has strong financials with stable revenue generation, double digit FCF yield. Macy’s generates over $1 bln in free cash flow and is expected to be cash positive for the foreseeable future. Targeting an adjusted EBITDA margin of 11.5-12% by fiscal 2024 and aims to generate $3 bln of FCF over the next 3 years.
Exhibit 3: Company historical financials and the consensus estimate
Company historical financials and the consensus estimates (Bloomberg, Analyst research)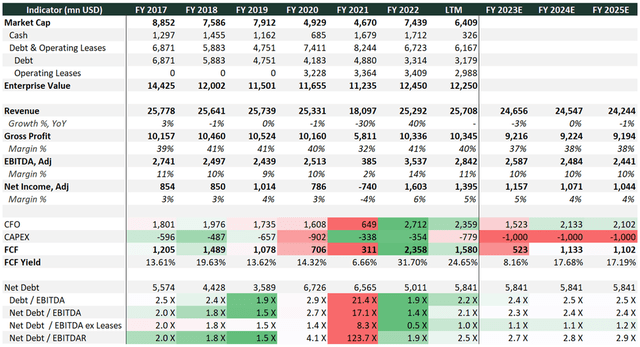
Source: Bloomberg, Analyst research
Currently Macy’s has a moderate level of debt burden reducing net leverage to 2.1 X. Also, the level of interest coverage does not raise questions. Macy’s refinancing risk is low with the next major maturity in 2029 since that Macy’s did debt repayments in the first half of this year. This provides the company with the opportunity to gradually repay part of the long-term debt.
Exhibit 4: Debt distribution
Debt distribution (Earnings report)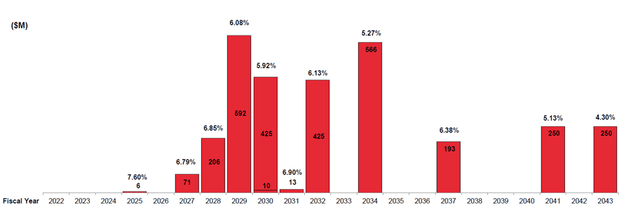
Source: Earnings report
Furthermore, Macy’s still has a strong liquidity position despite C&CE reduction compared with last year. Total liquidity is around $3.2 bln including cash and $2.9 billion of availability under its ABL.
This financial year company resumed capital distribution to current shareholders via dividends and buybacks. As we can see from the Graph below, Macy’s has been distributing dividends to shareholders since 2004, with a COVID-related pause in 2020-2021.
Dividends: For now, Macy’s pays a quarterly dividend of $0.16 per share, which translates to about $180 mln in annual spendings or an annual yield of about 3.8%.
Buybacks: We note Macy’s completed about $600 million of share buybacks in 2022. It has $1.4 billion authorized for the year and showed on the last earnings call the commitment to distribute CF to investors.
Capex: Macy’s expects to spend $1 billion in CAPEX in 2022, significantly higher than the approximately $600 million in 2021. High future CAPEX expectations are reflecting the investments the company is making to improve omnichannel capabilities and strengthen competitive positioning in the marketplace. These expenditures are expected to be financed with CFO and existing C&CE.
Exhibit 5: CF distribution (LTM)
CF distribution (LTM) (Bloomberg, Analyst research)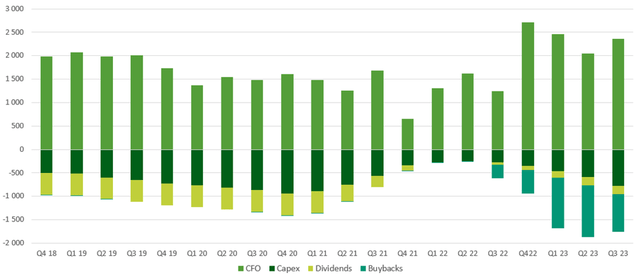
Source: Bloomberg, Analyst research
In addition, Macy’s successfully managed inventory levels compared with Kohl’s and Nordstrom. Inventory grew 4% YoY or down 12% relative to 2019. Management noted inventory that it strategically bought in seasonal merchandise earlier to strengthen its competitive position for holidays and has added the capacity to chase in-season trends.
Exhibit 6: Inventory turnover
Inventory turnover (Bloomberg, Analyst research)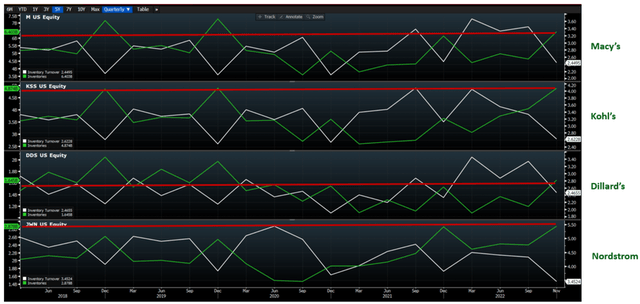
Source: Bloomberg, Analyst research
Besides every time in the last 8 quarters, Macy’s beats Bloomberg estimates consistently, and it does not disappoint investors during the reporting season. Furthermore, I should mention that there were only upward revisions of target prices as well as financial estimates.
Exhibit 7: Bloomberg consensus estimates
Bloomberg consensus estimates (Bloomberg, Analyst research)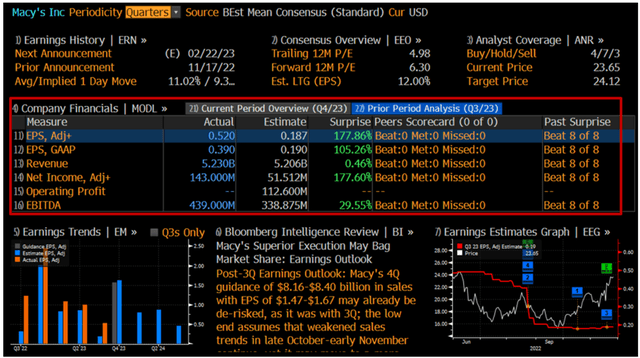
Source: Bloomberg, Analyst research
Furthermore, I should mention that there were only upward revisions of target prices as well as financial estimates.
Exhibit 8: Bloomberg consensus EBITDA 2024
Bloomberg EBITDA 2024 estimates (Bloomberg, Analyst research)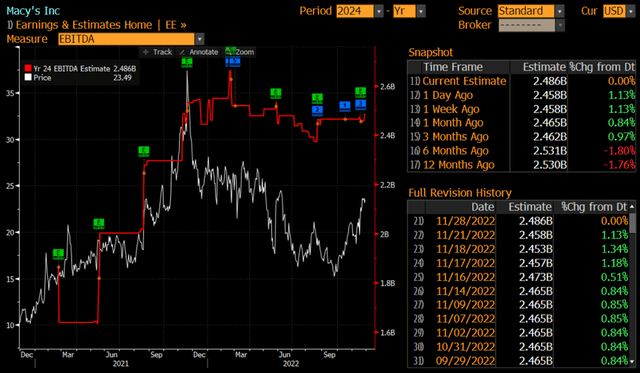
Source: Bloomberg, Analyst research
Speaking about credit quality metrics, Macy’s feels much better compared with the main competitors in the person of Kohl’s and Nordstrom. Macy’s leverage and margins have improved relative to peers Kohl’s and Nordstrom, but they will all face pressure if consumer demand wanes and inventory levels remain elevated, combined with higher costs.
Exhibit 9: Credit metrics
Credit metrics (Bloomberg, Analyst research)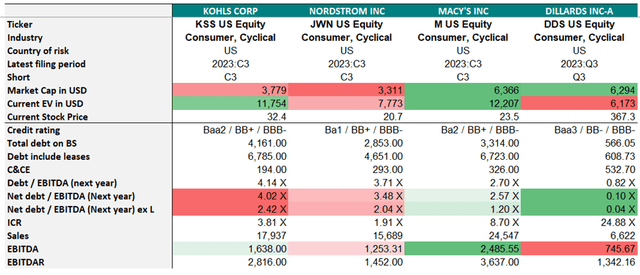
Source: Bloomberg, Analyst research
Furthermore, CFO on the last earnings call confirmed that they are targeting a leverage ratio below 2 X on an adjusted basis which indicates the company’s determination to further reduce the debt burden.
Polaris strategy
Macy’s is benefiting from implementing Polaris strategy. The latter is announced in February 2020 and aimed to stabilize profitability and position the company for long-term growth. The main growth points are:
- Strengthen customer relationships
- Curate quality fashion
- Accelerate digital growth
- Optimize store portfolio
- Reset cost base
Based on the results of three years, we can say that most of the goals were achieved by the end of 2022, Macy’s saved almost $1 billion in SG&A expenses, increased Ecommerce for 31% of sales and the number of economically ineffective stores were reduced. From all of the above, actuality Macy’s strategy works well and changed the business model in the right direction.
Macy’s properties
Another thing that makes you believe in Macy’s is a large portfolio of diverse real estate properties. Its evaluations are slightly different, but impressive anyway. For instance, Cowen assessed the Macy’s real estate holdings to be worth between $6 billion to $8 billion alone, while analyst from Evercore suggests it is worth $7 billion.
Thus, Macy’s is broad portfolio of Macy’s debt and has a low risk, being backed by 2x real estate value and stable earnings.
Exhibit 10: Macy’s Herald Square in NY city
Macy’s Herald square in NY city (Macy’s website)
Source: Macy’s website
Power of brand
It should be mentioned that Macy’s also has strong brand awareness and power. The company ranked 67 places out of 100 most powerful brands. Macy’s brand can compete with HP in hardware, Boeing in the aviation industry, or Ralph Lauren in the apparel business. We reckon that Macy’s brand is worth several times more than the current valuation what also pleases us as bondholders. Even if a distressed scenario occurs, there will be plenty of debtholder interest in Macy’s valuable brand.
Strong industry expertise
In addition, it should be noted that Macy’s management consists of professionals, who have been in business for more than a decade with wide experience in other industry giants such as Walmart and Target. Furthermore, the key focus for the group now is strategic rebuilding and shifting focus from traditional business to e-commerce. This thing is highly related to being highly dependent on CTO performance. Given the relevant experience and the work done, everything should work out.
Exhibit 10: Management team
Management team (Annual report)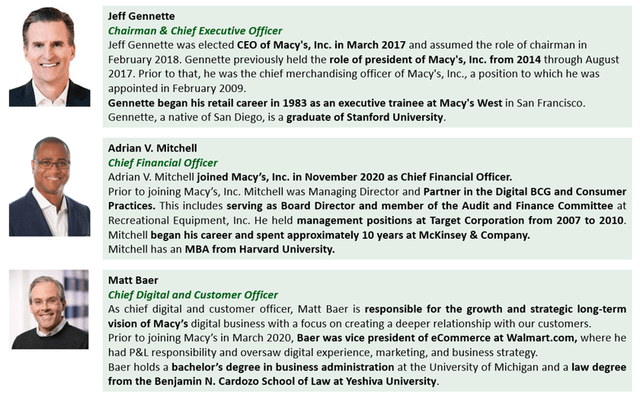
Source: Annual report
Bonds selection
For now, we can declare with full responsibility that Macy’s currently is one of the most interesting fixed-income ideas. The company is large enough and stable enough to go through problems. Below I could find the table of active bond issued of Macy’s.
Exhibit 12: bond issues
Bond issues (Bloomberg, Analyst research)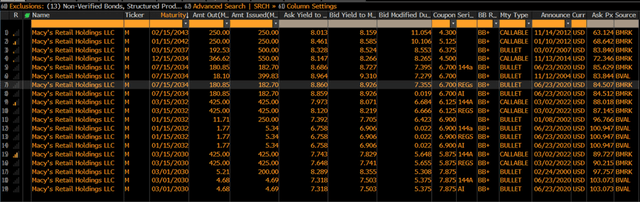
Source: Bloomberg, Analyst research
If the Fed funds rate ends up peaking at 5%, this implies that the 10-year yield will peak between 4-5%, higher than its current level. The cyclical peak in bond yield happens within a narrow window of the last Fed rate hike from -4 to +4 months until the last rise.
Exhibit 13: month between the last hike and the peak in the 10 UST yields
month between the last hike and the peak in the 10 UST yields (BCA research)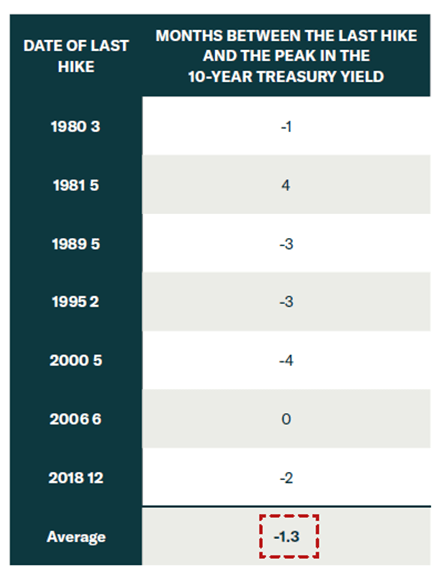
Source: BCA research
Now the swap market is pricing a rate hiking cycle end in April-May next year, which gives time to buy longer bonds, but things can change quickly after new CPI releases.
Exhibit 14: US interest rate probability
US interest rate probability (Bloomberg, Analyst research)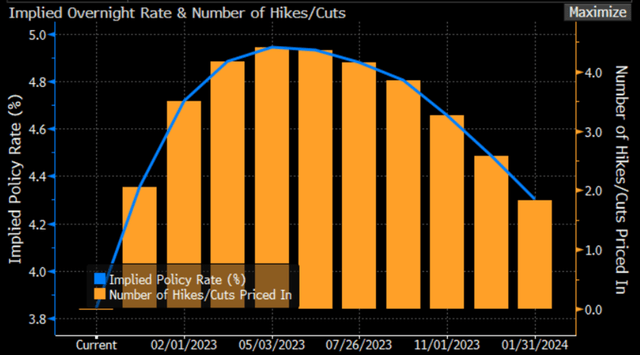
Source: Bloomberg, Analyst research
Undoubtedly, it’s extremely complicated to find the bottom in that quickly changing economic environment with many inputs, but from our point of view now you can start to find an entry point in bonds with increased duration. This Macy’s bond issue certainly belongs to the latter.
Exhibit 14: security description
Security description (Bloomberg, Analyst research)
Source: Bloomberg, Analyst research
Investor takeaways
Macy’s remains the best option to buy in the fixed income universe in the department store segment. We’re overweight Macy’s bond issue with 10-years duration due to high exposure to interest change and strong financials, which still provide confidence with a large portfolio of diverse real estate and brand recognition.
Key risks
- Macy’s started capital allocation to shareholders via buybacks & dividends and committed to increase CAPEX program by 40% which likely will reduce FCF generation.
- Weakening consumer demand and rising costs.
- Lower margins due to increased promotions as well as inflationary pressure related to product costs and wages.
- Macy’s ability to hit fashion trends, weather trends.
- Longer maturities have greater interest rate risk, which is an important consideration in a period when interest rates appear to be rising.


Be the first to comment