Bet_Noire
By Sonal Desai, Ph.D., Chief Investment Officer, Franklin Templeton Fixed Income
Are we there yet? Fed Chairman Jerome Powell hedged himself carefully at the July press conference; markets heard it as confirming expectations that we are closing in on the terminal rate and that the Fed will likely start cutting again as early as March of next year. Our Fixed Income CIO Sonal Desai is not so sure—here are her thoughts:
US Federal Reserve (Fed) Chairman Jerome Powell hedged himself very carefully in the press conference following the July 27 Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting. Financial markets heard only what they wanted to hear and ignored the rest. Markets chose to hear that the “Fed put” is alive and well, and it fueled a rally in both equities and bond yields. I think this just sets the stage for a correction, and more volatility ahead.
Powell said that policy interest rates are now in the neutral range (I disagree, but more on this later), the economy has started to weaken, and that the full impact of the rate hikes delivered so far has yet to be felt. This reinforced the markets’ conviction that we are approaching the peak of the tightening cycle, and that by the first quarter (Q1) of next year, the Fed will reverse course and start cutting rates. Indeed, markets now expect 50 basis points (bps) of rate cuts next year.
Franklin Templeton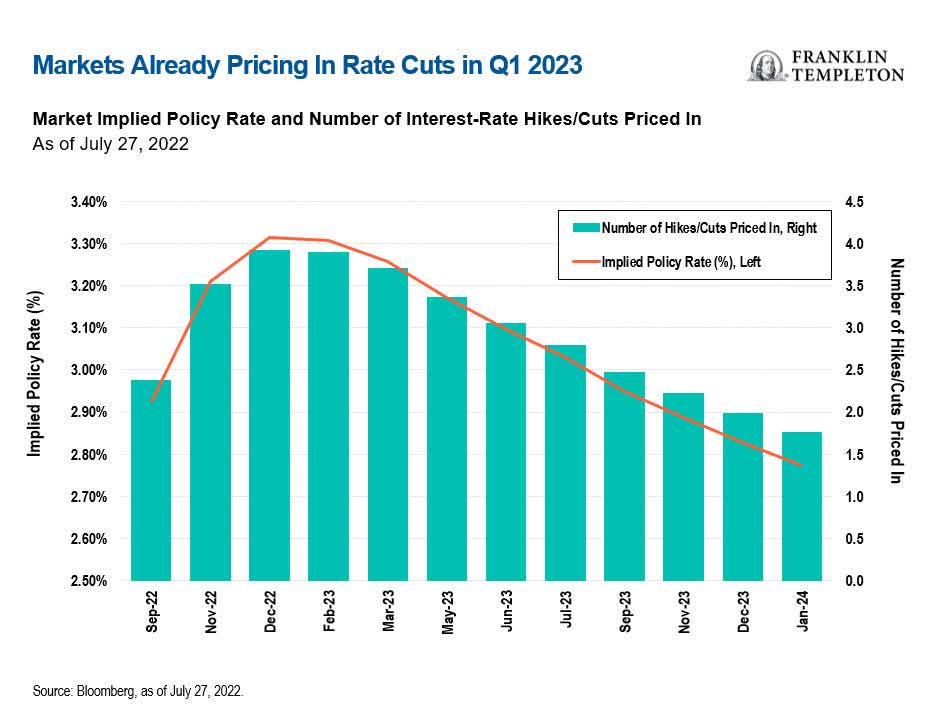
But Powell also said that the FOMC’s June views on the likely path of rates still stand, and those views suggest the Fed would keep hiking into 2023 to a peak of about 3.8%. Powell noted that another “unusually large” rate hike in September could not be ruled out. He underscored the persistent strength of the labor market and said that bringing inflation back to target will require slower growth and higher unemployment. So far, markets do not seem to have paid much attention to that part.
Commenting on the June press conference, I had noted that the Fed had de facto abandoned forward guidance; today, nearly all commentators agreed that forward guidance is gone, as Powell was even more emphatic in stressing that uncertainty is high, the Fed has very little visibility and will choose its next moves meeting-by-meeting as new data come in.
I think Powell could have been more forceful in indicating that, with inflation at 40-year highs and unemployment at 50-year lows, the Fed has a ways to go to bring demand and supply back in balance and restore price stability. But—as he admitted—the Fed’s previous forecasts of how quickly inflation would fade have proved totally wrong, so we can’t fault him for taking a humbler and more data-dependent stance.
This, however, makes the Fed’s job more complicated to the extent that the rally in equities and the decline in bond yields drive a meaningful easing in financial conditions, undoing part of the Fed’s work. Moreover, I continue to disagree with the Fed on the neutral interest rate: I don’t think the neutral range is as low as 2.0%–2.5% in nominal terms—and by the way, we’re talking about the rate that would be neither restrictive nor expansionary with US inflation at 2%, not with inflation at the current 9%. Meanwhile, the labor market remains hot and activity fairly resilient, partly thanks to robust household balance sheets.
Overall, while we might get some help from lower gas prices in the next print, I think underlying inflation will remain stubbornly high for the remainder of the year. Importantly, higher than markets think and the Fed hopes. This, in turn, should compel the Fed to keep hiking into next year. I think the terminal rate will be much closer to having a “4” handle; but even if the Fed stops below that, I believe it will have to keep rates at their chosen plateau through a large part of next year to convincingly rein in inflation. The idea that a steep easing cycle could start as early as Q1 2023 seems far-fetched, in my view.
WHAT ARE THE RISKS?
All investments involve risks, including possible loss of principal. The value of investments can go down as well as up, and investors may not get back the full amount invested. Bond prices generally move in the opposite direction of interest rates. Thus, as prices of bonds in an investment portfolio adjust to a rise in interest rates, the value of the portfolio may decline.
Editor’s Note: The summary bullets for this article were chosen by Seeking Alpha editors.


Be the first to comment