Justin Sullivan
When it rains, it pours – and that seems to be NVIDIA’s (NASDAQ:NVDA) case recently. The broad-based market selloff this year has already weighed on the NVIDIA stock this year, with valuation multiples contracting violently across the semiconductor sector as investors’ concerns about a structural “bust” after a multi-year boom increase ahead of a looming economic downturn. And NVIDIA’s market value fell another leg lower when its fiscal second quarter results broke a multi-quarter streak of outperformance, validating market worries that its near-term prospects will be shaky. Despite NVIDIA’s earlier confidence that momentum in data center and auto demand will make up for some of the near-term weakness across the consumer and enterprise GPU markets (i.e. gaming and professional visualization segments), the U.S. government’s recent decision to restrict export of certain semiconductor technologies to China – one of NVIDIA’s largest end markets – risks severing the chipmaker’s last respite.
Yet, considering NVIDIA’s technologies remain the backbone of critical next-generation digital trends, its long-term fundamental outlook remains intact. But with the near-term performance of NVIDIA’s four core business segments being a big question mark, alongside broader uncertainties over the macroeconomic outlook (e.g. Fed tightening trajectory, inflation, recession, etc.), volatility will likely remain the theme for its shares over coming months.
Overview of Licensing Requirements on Semiconductor Exports to China
The U.S. government has been proactively rolling out legislation – supportive of the build-out of domestic semiconductor technology production and development capabilities on home soil in recent months as part of ongoing efforts to bolster competition against China and rein in the latter’s influence within the increasingly constrained industry. Following the recent introduction of the CHIPS Act, which allocates $52 billion towards the build-out of chip manufacturing capacity in the U.S., the government has now decided to further limit China’s “access to AI products as well, [creating] another chokepoint for Beijing’s tech expansion”.
Under the recent licensing requirements imposed on certain next-generation AI-enabling hardware – a field in which NVIDIA dominates and commands 95% of the market share – chipmakers would need to obtain approval before any units are exported to China. This includes restrictions on NVIDIA’s best-selling Ampere architecture-based A100 server GPUs, as well as its newest Hopper architecture-based H100 server GPUs shipping later this year:
In a separate filing on Thursday, Nvidia said the US government has authorized it to “perform exports needed to provide support for US customers of A100 through March 1, 2023.” Nvidia has also been granted permission to transfer necessary technology to China for the development of its upcoming H100 products. These exports are authorized to be conducted through the US chipmaker’s Hong Kong facility through Sept. 1, 2023, according to the filing.
Source: Bloomberg
With China being one of NVIDIA’s largest end-markets, contributing to almost a quarter of the chipmaker’s revenue mix, the latest restrictions imposed by the U.S. government risks further uncertainties to its near-term fundamental outlook. This is further corroborated by the company’s recent underperformance, which was partially caused by deterioration in the Chinese economy due to stringent COVID restrictions in the region.
Data Center Impact
NVIDIA’s data center segment sales have long been a highlight and core driver of its outperforming growth in recent years. Despite heightened supply constraints during the fiscal second quarter, which saw its data center revenues falling short of initial expectations, the segment’s sales continued to climb towards new records with solid double-digit y/y growth. Management has also previously relied on continued momentum in data center sales to partially compensate for the near-term weakness in gaming and professional visualization segment performance, guiding sequential growth in the current quarter. Yet, the U.S. government’s latest restrictions imposed on semiconductor technology exports to China risk derailing said plans.
China remains a critical market for NVIDIA, representing close to a quarter of its sales in recent reporting periods. NVIDIA’s sensitivity to disruptions within its China market from a fundamental perspective is portrayed via the company’s slight underperformance in the fiscal second quarter, which was partially driven by adverse impact from the region’s ongoing COVID restrictions that have both limited demand and intensified supply constraints:
Let me answer the questions about the North American and the China hyperscalers. The Chinese hyperscalers and the Chinese Internet companies really, really slowed down infrastructure investment this year, particularly starting in — they’ve been rather slow in building out and really accelerate — well really slowed down in Q2. This slowdown can’t last forever. And the number of new technologies in software, the number of people who are using clouds and the number of cloud services is continuing to grow. And so I fully expect investment to return. They’re a very important market for us, a very large market for us. And the fact that North American hyperscalers doubled year-over-year our revenues at North American hyperscalers, and that was offset by declines in China said something about the slowdown in China.
While NVIDIA has recently touted the importance of its new Hopper-based server processors in facilitating “transformer models”, which are one of the newest types of AI models capable of complex tasks like “translating text and speech in near real-time [and] helping researchers understand the chains of genes in DNA and amino acids in proteins”, its H100 chips have been identified as a technology restricted from export to China under new rules established by the U.S. government. For now, the U.S. government has granted NVIDIA approval to “transfer necessary technology to China for the development of its upcoming H100 products”, which are expected to start shipping substantially in the fourth quarter. Exports of related technologies to China have also been authorized until September 1, 2023. The chipmaker would be required to obtain “approval from the U.S. government before they can be sold to Chinese customers” thereafter, underscoring the uncertainties ahead pertaining to its core driving market.
Similar restrictions have been levied on NVIDIA’s currently best-selling A100 data center GPUs built on its existing Ampere architecture. Under the new rules, NVIDIA would be restricted from exporting said chips to China after March 1, 2023 unless approval is obtained from the U.S. government.
As the market leader in GPUs and AI processors, NVIDIA’s exposure to adverse impacts stemming from the U.S. government’s latest regulatory changes is comparatively substantial when punt against rivals like AMD (AMD), Broadcom (AVGO), and/or Intel (INTC). With more than a quarter of its annual sales generated from China last year, or more than $7.1 billion, NVIDIA accounts for about 3% of $212 billion worth of chips sold to the region in calendar 2021. The company currently anticipates $400 million in lost revenues due to impacts from the newly imposed export restrictions in the current fiscal quarter alone, which potentially wipes out earlier hopes of sequential gains in data center sales over the same period, while introducing longer-term uncertainties until there is further clarification on the extent of export authorization NVIDIA will be granted on A100 and H100 chip exports next year.
Automotive Impact
After multiple consecutive quarters of either deceleration or declines in chip sales to auto OEMs due to industry-wide supply chain constraints, NVIDIA’s automotive segment started to see momentum pick up in the fiscal second quarter. Related sales rose 45% y/y and 59% sequentially to $220 million, buoyed primarily by its “NVIDIA DRIVE” offerings used in facilitating autonomous and connected mobility. During the fiscal second quarter earnings call, management had alluded to an “$11 automotive design win pipeline” that is expected to drive longer-term growth. Yet, this momentum is expected to experience some bumpiness ahead, as much of it is supported by partnerships with Chinese OEM partners, with the most notable being NIO (NIO), Li Auto (LI), XPeng (XPEV), JIDU, Human Horizons, as well as BYD (OTCPK:BYDDF / OTCPK:BYDDY). Even XPeng founder and CEO He Xiaopeng have recently expressed concerns about the future of autonomous vehicle technology development under the newly imposed U.S. chip export restrictions, underscoring the severity of uncertainties over how U.S.-China chip relations will play out:
The measures will “bring a challenge to the cloud training of all autonomous driving,” He Xiaopeng, the chairman and chief executive officer of XPeng Inc., said on his WeChat account. Nvidia is a leader in providing the hardware for autonomous driving — both for developing the algorithms in massive server farms and supplying the onboard processors for cars to be aware of their surroundings.
Source: Bloomberg
While the U.S. government has yet to disclose any export restrictions specific to NVIDIA DRIVE solutions, related regulatory risks remain a major overhang over the company’s next core growth driver. Although the automotive segment currently represents only a nominal portion of NVIDIA’s total sales mix, it has been viewed with high hopes as the next fastest-growing business for the company. This is because of the “mission critical” role that NVIDIA’s end-to-end hardware-software offerings play in the ongoing development of autonomous driving capabilities, an emerging technology trend that is expected to unlock a $60+ billion total addressable market by 2030:
Our automotive revenue is inflecting, and we expect it to be our next $1 billion business. Autonomous driving is one of the biggest challenges AI can solve, and computing opportunity for us spans the data center to the car. Autonomous driving will transform the auto industry into a tech industry. Automotive is one of the first to transform into a software-defined tech industry that all industries will be.
Sensitivity Analysis – Fundamental Forecast
To further gauge the anticipated impact of newly imposed rules on NVIDIA’s near-term valuation prospects, we have performed a sensitivity on the company’s fundamental outlook under three scenarios:
- Bull case: This maintains the same key assumptions discussed in our most recent analysis on the stock, which takes into consideration NVIDIA’s historical fundamental performance, adjusted for actual fiscal second quarter results and fiscal third quarter guidance, as well as its operating environment’s outlook based on forward market trends. Bull case assumptions applied expect the company’s China operations to continue as is, without material adverse impact from the newly imposed chip export ban beginning early 2023.
NVIDIA Bull Case Financial Forecast (Author)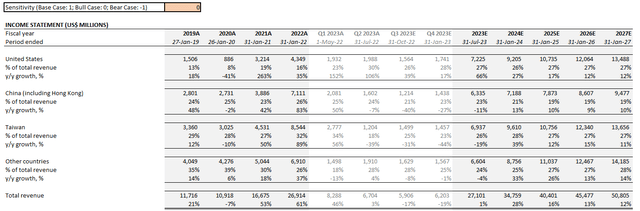
- Base case: Our base case forecast now discounts anticipated China revenues in the bull case forecast by 25%, which is consistent with estimated lost sales of $400 million in the current fiscal quarter as a percentage of prior quarter sales in the region due to the newly-imposed export restrictions according to NVIDIA management. As a result, consolidated revenues are expected to expand at a five-year CAGR of 12.7% from $26.2 billion in fiscal 2023 towards $47.6 billion by fiscal 2027. Anticipated growth from all other regions in operations (i.e. U.S., Taiwan, and Other Countries) are held constant from our bull case forecast.
NVIDIA Base Case Financial Forecast (Author)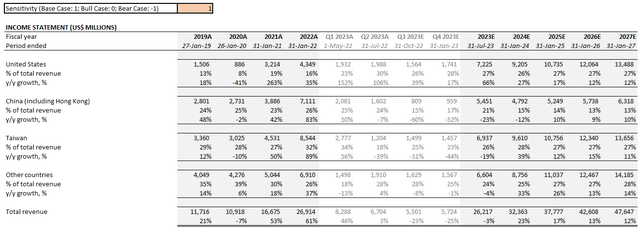
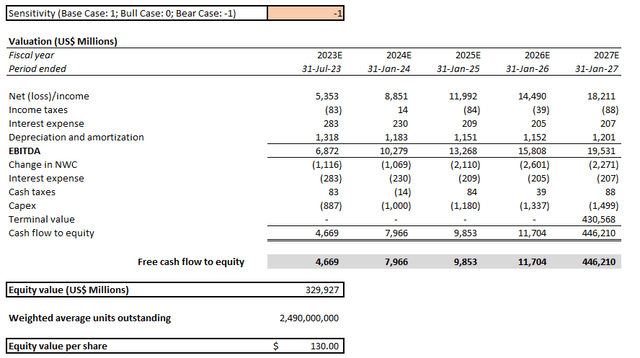
- Bear case: In the worst-case scenario where NVIDIA would be required to exit China completely, consolidated company revenues are expected to expand at a moderated five-year CAGR of 11.1% from $24.4 billion in the current fiscal year towards $41.3 billion by fiscal 2027. Anticipated growth from all other regions in operations (i.e. U.S., Taiwan, and Other Countries) are held constant from our bull case forecast.
NVIDIA Bear Case Financial Forecast (Author)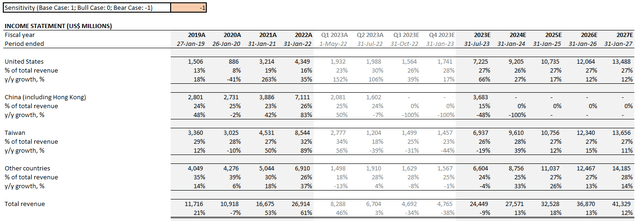
Sensitivity Analysis – Valuation
NVIDIA Valuation Analysis (Author)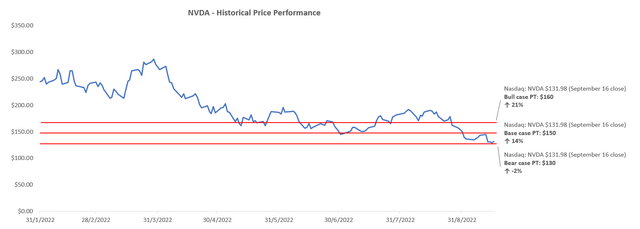
Drawing on the above fundamental forecasts sensitized for varying degrees of adverse impact from recently imposed chip export restrictions to China by the U.S. government, paired with the near-term contraction in valuation multiples observed across the semiconductor industry, our base case price target for the NVIDIA stock is set at $150. This represents upside potential of 14% based on the stock’s last traded price of $131.98 on September 16. The valuation analysis assumes an exit multiple of 22.1x EV/EBITDA, which represents a perpetual growth rate of 8%, consistent with market expansion across core technology trends in which NVIDIA plays a critical role in, as well as a premium to reflect its market leadership in the provision of graphics processors and AI developments.
NVIDIA Base Case Valuation Analysis (Author)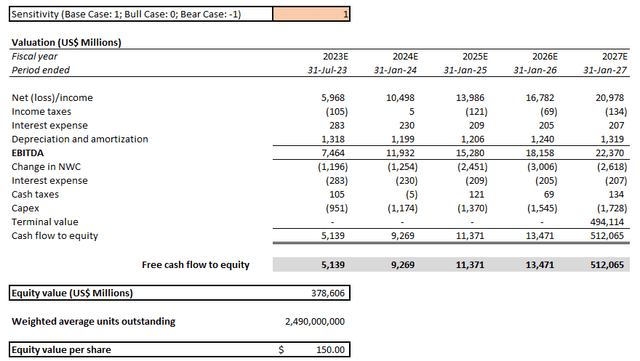
Our bull and bear case price targets are $160 and $130, respectively, based on the fundamental forecast scenarios discussed above while holding key valuation assumptions constant. Based on the proximity between our bear case price target and the current market price for NVIDIA shares, market is likely already starting to price in the anticipated worst-case scenario in the near term with respect to the company’s business prospects in China under U.S.-levied export restrictions.
NVIDIA Bull Case Valuation Analysis (Author) NVIDIA Bear Case Valuation Analysis (Author)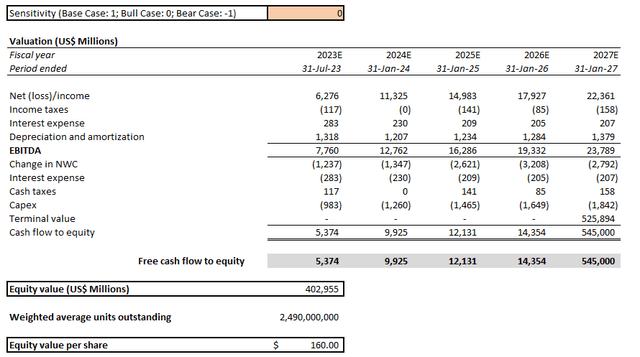
Final Thoughts
NVIDIA’s offerings remain the backbone of critical next-generation technologies, spanning cloud-based computing to complex AI capabilities applied across a wide range of use cases from genetic sequencing to autonomous mobility. Yet, with China being a core market to NVIDIA, the company faces inevitable adversity to its near-term fundamental performance, the degree of which remains an uncertainty until further details to how the export restrictions will be enforced come to light. As a result, NVIDIA’s prior growth realization trajectory is expected to become lengthened, given anticipated disruptions to its core market operations, depending on how intensifying U.S.-China geopolitical tensions unfold as its business gets caught in the cross-fire.
Related regulatory risks are expected to remain a near-term pressure on the NVIDIA stock’s performance, which warrants caution. However, while its growth trajectory is slowed with its market size expected to shrink under the worst-case scenario where the U.S. government severs ties with China in terms of critical co-developments in chip technologies, NVIDIA remains the undisputable market leader in the provision of core processors used in enabling critical digital infrastructures both within the foreseeable future and over the longer term. As such, the stock’s long-term bullish narrative likely remains structurally intact, buoyed by its market leadership in enabling development of critical next-generation technologies, which makes it a favorable long-term investment still ahead of anticipated lower levels over coming months.


Be the first to comment