martin-dm
Article Thesis
NVIDIA Corporation (NASDAQ:NVDA) has seen its shares pull back massively in recent months. Shares are now trading at a discount compared to where they traded historically, for the first time in many years. Fear about its future has gripped the market, but NVIDIA’s long-term outlook is compelling since the long-term growth drivers remain in place. NVIDIA faces some short-term headwinds such as the crypto winter but should be a profitable investment at the current valuation for those that have a multi-year investment horizon.
NVIDIA’s Long-Term Growth Will Likely Continue
NVIDIA has experienced massive business growth in the last couple of years, and that should be the case in the future, too. Growth will likely slow down on a relative basis, but that is to be expected from every company, as the law of large numbers dictates that maintaining extraordinary relative growth rates becomes impossible at some point. But revenue growth of 30%, 50%, or even more per year is not needed for NVIDIA to be a good long-term investment. In fact, I do believe that even a 10% or 15% annual revenue growth rate could lead to compelling total returns for NVIDIA’s shareholders when they hold for a long-enough time frame.
Where will that growth come from? NVIDIA benefits from several macro trends that continue to grow its addressable market. The first one is data centers. Here, NVIDIA competes with AMD (AMD) and Intel (INTC) primarily. According to GMI Research, the global data center market will grow by 12% a year through 2028, which allows for solid baseline growth in a scenario where NVIDIA does not take any market share from its competitors. That’s not my assumption, however. Instead, I do believe that NVIDIA will continue to grow its data center business at an above-market growth rate thanks to its attractive offerings in this space. NVIDIA’s HGX-1 hyperscale GPU accelerator, powered by eight NVIDIA Tesla GPUs, is the world’s fastest product in its class. Its industry-leading performance makes it attractive for hyperscale data centers that can rely on its computing power, while cost advantages also make it attractive for buyers:
NVIDIA website
HGX-1’s performance especially shines in deep learning and other AI-related tasks, where it outperforms traditional CPUs by up to 10,000%. With inflation hurting the margins of many companies, and with a potential recession eating into their growth outlook, many companies have become more focused on bringing down expenses and becoming more efficient (such as Meta Platforms (META) and Alphabet (GOOG)). With these major cloud computing players focusing more on efficiency and profitability, NVIDIA’s massive cost advantages in machine learning and other AI-related tasks should be a huge selling point for its HGX-1 and similar products. In a recession, when cost controls are highly important, the most cost-efficient product should be especially attractive, which should help NVIDIA grow its market share.
NVIDIA’s management also is positive when it comes to the company’s growth outlook in the data center space. In the most recent earnings call, NVIDIA’s EVP and CFO Colette Kress stated that “Data Center has become [NVIDIA’s] largest market platform, and we see continued strong momentum going forward” [emphasis by author].
During the most recent quarter, data center revenue totaled $3.8 billion, or around $15 billion annualized. That was up 15% on a sequential basis, and up more than 80% year over year. Growth will not always be this high, of course, but with NVIDIA’s strong product lineup and the strong momentum its CFO has hinted at, investors can probably expect that the data center business will remain a major growth driver going forward.
Data centers are not the only attractive market for NVIDIA. The company is also well-positioned to benefit from a massive increase in high-end chip demand from the automobile industry. Automobiles have been using chips for many years, but the number of chips per vehicle and the power (and cost) of those chips are not static. While traditional cars didn’t use a lot of chips in the past, and while those chips generally weren’t very capable and thus pretty cheap, things are changing due to two megatrends.
First, electric vehicles use more chips than ICE-powered vehicles, due to additional tasks such as battery management. Even more importantly, the young but accelerating trend of autonomous vehicles increases the number of chips per car and requires much more powerful chips. More powerful chips naturally cost more and do thereby create a way larger revenue opportunity for suppliers to the automobile industry. Autonomous vehicles, or semi-autonomous vehicles, need to gather gigantic amounts of data via cameras, LiDAR, and so on. That data has to be processed very quickly, as (semi-) autonomous vehicles need to make decisions in split seconds.
NVIDIA is one of the suppliers of high-powered chips that can do this task, via its lineup of autonomous-focused products. The DRIVE Orin SoC is one such product that has gone into production earlier this year. The SoC has gotten a lot of attention from potential customers, and more than 35 customer wins have been announced to date. This includes major wins such as from Buffett-backed BYD (OTCPK:BYDDY), which is China’s biggest EV player and a major competitor to Tesla (TSLA). Lucid (LCID), which isn’t very large yet but has received a lot of praise for its exceptional tech, has also agreed to use DRIVE Orin in its vehicles. CFO Colette Kress explains that NVIDIA’s “automotive design win pipeline now exceeds $11 billion over the next six years, up from $8 billion just a year ago” (see link above). Year-over-year growth of close to 40% is great, and over time, that business should become way more impactful for NVIDIA’s top and bottom line. So far, one can argue that revenue contribution isn’t very large – $11 billion over six years is around $2 billion a year. But if growth remains sky-high, the autonomous business will likely become highly important in a couple of years. Due to the massive market growth for autonomous driving chips and due to NVIDIA ramping up its product line in this space and seemingly adding new customers every week, I do believe that there is a high likelihood of growth in this space to remain very strong for years to come.
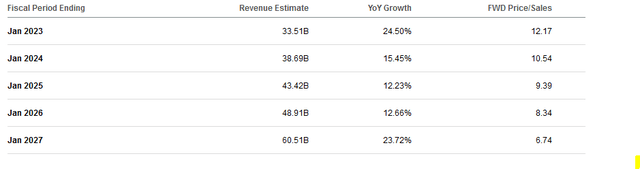
Analysts believe that NVIDIA’s revenue growth could look like this in the coming years:
25% growth this year would still be very strong, while growth in the following years will slow down to a 10%-15% range – if Wall Street is correct. The forecast for 2026 (ending January 2027) sees an acceleration towards the mid-20s again, but there are fewer analysts with estimates for that year, so this estimate likely is more uncertain compared to the next couple of years.
Even revenue growth of 15% or so would be sufficient to generate compelling longer-term returns, however. NVIDIA should, like most other companies, benefit from some margin expansion when it continues to grow its revenue. Operating leverage dictates that operating expenses, such as those for administration, should decline as a percentage of revenue and gross profit as a company grows over time. Net profit can thus be expected to grow somewhat faster than NVIDIA’s revenues. On top of that, since NVIDIA has a clean balance sheet and a low dividend payout ratio, the company has ample surplus cash that can be used for other purposes, such as buybacks. NVIDIA has a $15 billion buyback program in place, which is enough to repurchase 4% of the company at current prices. Over time, these buybacks will add meaningfully to NVIDIA’s earnings per share growth and its total return potential.
A Look At NVIDIA’s Valuation And Risks
NVIDIA traded for as much as $350 over the last year, which was not justified. But since then, shares dropped by more than half. Today, NVIDIA trades well below the historic valuation norm:
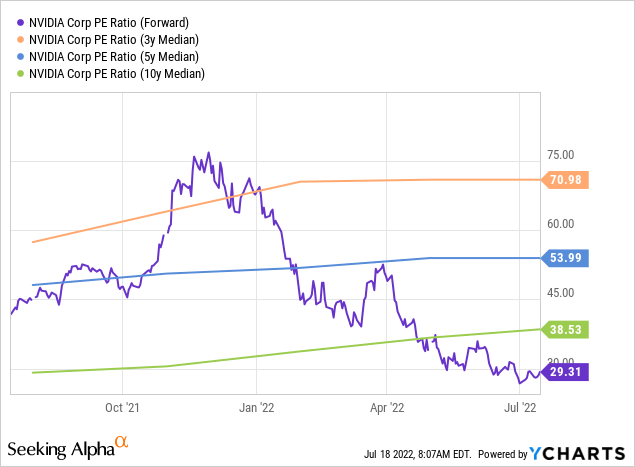
At 29x net profit, NVIDIA is valued at 25% less than the 10-year median earnings multiple. The discounts to the 5-year and 3-year earnings multiples are even larger, at around 50% and 60%, respectively. The market has cooled on NVIDIA, and it’s likely that greed is no longer the driving force for NVIDIA’s share price. Instead, some investors seem to be fearful, which is why NVIDIA has seen its share price drop so much in the last couple of months.
Panic selling by some investors can provide attractive entry points for other investors, and I do believe that such a buying opportunity is emerging. With NVIDIA trading for 29x forward earnings, while still growing at a compelling rate, the total return outlook is pretty solid. If NVIDIA hits the $5.40 EPS estimate this year and grows its earnings per share by 17% a year over the following three years, before EPS growth slows down to 14% for 2026-2030, then EPS could total $16.70 in 2030. Put a 20x earnings multiple on that and you get a share price of $340 – which equates to an upside potential of more than 100% over the next eight years, even under rather conservative assumptions. EPS growth could be higher, especially when we factor in buybacks, and the valuation in 2030 could also be higher. I do thus believe that the current sell-off in NVIDIA provides a nice entry point for long-term investors.
Risks shouldn’t be neglected, however. The current crypto winter is a potential near-term headwind, as it may result in lower GPU sales in the coming quarters. In the long run, that should be more than balanced out by data center and autonomous growth, however.
NVIDIA’s reliance on foundries is another risk. Especially the exposure to Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSM) makes for macro risk exposure to a potentially escalating conflict in Taiwan. That will hopefully not happen, but if it were to happen, NVIDIA would be more exposed than many other companies.
Takeaway
NVIDIA’s shares have crashed, dropping by more than 50% from the 52-week high. This panic selling has made NVIDIA’s valuation drop to a below-average level, as shares are now trading at a clear discount compared to how the company was valued in the past. At the same time, its growth outlook is still very compelling and its buybacks will be more effective with shares trading at a lower valuation.
For long-term-oriented investors, the selloff, which was driven by panic around rising rates, a potential recession, etc., makes for a nice entry point. Shares should be able to double through 2030, and returns could be significantly higher as that estimate already accounts for further multiple compression.


Be the first to comment