deepblue4you/iStock via Getty Images
Global auto sales in the second quarter were largely lower than volumes in the first quarter as expected, considering pandemic disruptions in key auto manufacturing hub Shanghai. The industry also continues to reel from prominent supply chain and logistic disruptions worldwide, with shipment delays on key materials – especially semiconductors – hampering production volumes from ramping up to capacity.
However, significant improvements in June underscore the resilience of the electric vehicle (“EV”) industry, as well as the broader automotive sector in the event that global supply chain bottlenecks continue to ease. Most auto OEMs have also reiterated their full-year production targets, implying that it will be a back-end weighted year for the industry, barring no unexpected material disruptions to business through the rest of the year.
And despite looming recession risks, the industry has yet to sound alarms on any signs of demand destruction – EV makers continue to benefit from a still-robust demand environment buoyed by continued improvements to battery technology, increasing availability of global public charging infrastructure, rising prices at the pump, roll-out of new models to accommodate different consumer preferences and budgets, and favourable policy environment.
Nonetheless, investors will likely look to management in the upcoming earnings season for clues on margin expansion outlook under a still-constrained supply environment, which translates to higher input costs, alongside a potential slowdown in demand that risks hampering top-line growth in the near-term. While valuation multiples across the entire EV sector have already compressed significantly from their all-time highs in the first half of 2022 due to concerns of stalling growth and value erosion on future earnings amidst rising interest rates, the selloff is likely not over as investors now pivot their attention to margin erosion from persistent inflationary pressures. Similar to observations in the past two quarters, investors will continue to expect nothing short of the average consensus estimate, if not outperformance, to justify their bullishness under the current risk-off environment for equities. Alternatively, any hint of weakness will be sufficient to unleash another round of selloffs.
Performance Preview by Region
U.S.
Second quarter auto sales in the U.S. were largely muted due to production challenges from the ongoing chip shortage, a situation that remains fluid. Auto sales decreased in both April (1.26 million units sold; +0.5% m/m; -18% y/y) and May (1.12 million units sold; -11.2% m/m; -29.9% y/y), while June delivered slight improvements (1.15 million units sold; +2.8% m/m; -12% y/y).
Meanwhile, EV demand remains robust despite increasingly hefty price tags. Thanks to the ongoing improvement in battery technologies, increase in availability of public charging infrastructure, favourable policy support, roll-out of new models to accommodate different consumer preferences and budgets, and now higher prices at the pump, EV adoption in the U.S. has continued to outpace legacy internal combustion engine (“ICE”) vehicle sales. While ICE passenger vehicle sales and light-duty truck sales (i.e. SUVs and pickup trucks) fell by 21.4% y/y and 9% y/y in June, respectively, new energy vehicle sales continued to soar. Specifically, hybrid vehicle sales represented 5.4% of total new car registrations in June, battery EVs 6.2%, and plug-in hybrid EVs 1%.
Looking ahead, slowing consumer spending and weakening consumer sentiment amidst surging inflation and rising interest rates might become a hard-to-ignore headwind for the auto industry in the second half of the year. Specifically, inflationary pressures and ongoing inventory shortages have incentivized automakers to raise sticker prices, effectively passing the burden onto budget-conscious consumers and evoking demand risks.
Europe
Europe car sales were down 20% y/y in April (830,447 new vehicles sold) and down 12.5% y/y in May (948,149 vehicles sold) – the 11th consecutive month of sales declines. While the official tally for June sales in Europe is not yet available, Germany has already reported an 18% y/y sales slump in June, with deliveries of only 224,558 vehicles in Europe’s largest auto market during the period.
However, in a similar cadence with the U.S., EV sales in Europe remained robust. EV sales in Europe accounted for 19% of total new car registrations in the region in both April and May, with absolute delivery volumes up 3% from the prior year.
The threatening combination of ongoing supply chain constraints and an inflation-driven slowdown in consumption continues to weigh on Europe’s auto industry, causing the full year sales forecast to come down time and again – predictions earlier in the year had forecast 9% y/y volume growth, but the region is now expected to deliver 9.8 million vehicles only by the end of the year, a 7.4% slump from prior year volumes. The worsening energy crunch in Europe also threatens to thwart productions in the region.
China
The region has consistently made headlines in auto news during the second quarter, with all eyes on developments regarding its COVID Zero mandate and related impact on production volumes. The country sold zero vehicles in Shanghai during the month of April, a month that marked the height of pandemic lockdowns in the country’s key manufacturing hub. Overall car sales across the country were also down 46% m/m and 36% y/y to its worse volume for the month of April in a decade, totalling a little more than 1 million vehicles. But EV sales in the country were resilient nonetheless, with April delivery volumes up 78.4% y/y (-37% m/m) to 282,000 vehicles.
May auto sales were also impacted due to continued COVID lockdowns across China at the time, with deliveries down 17% y/y to 1.86 million vehicles for the month (though a marked improvement from April). But again, the Chinese EV market proved resilient – EV sales in China jumped 109% y/y in May to more than 400,000 units delivered. Momentum continued into June as well, with retail EV sales topping 546,000 units (+130% y/y) across the country.
China EV sales are expected to maintain its resilience through the back-end of the year, despite increasing signs of an economic slowdown in the country – the CPCA is now forecasting EV sales of 5.5 million units this year, up 90% from the prior year. Much of the sector’s growth has been buoyed by rapid adoption amidst a supportive policy environment. In addition to a slew of accommodative policies introduced by local governments in Shanghai and Beijing to shore up auto sales in recent months, the Chinese State Council Information Office also issued an official statement outlining its support for “promoting sales of new energy vehicles and ensuring the supply of auto chips and related raw materials with a relatively stable price”.
Performance Preview by OEM
Prominent EV pureplays within our coverage that is currently in productions include Tesla (TSLA), Rivian (RIVN), Lucid (LCID), Polestar (PSNY), NIO (NYSE:NIO), and XPeng (XPEV). All of which have showed resilient production and delivery volume improvements in the second quarter despite still-constrained global supply chain that have been further exacerbated by protracted COVID disruptions in China.
While expectations for second quarter delivery and production volumes have been muted compared to previous periods to account for known production and supply chain challenges, investors are most looking forward to a back-end weighted year. Ahead of the upcoming earnings season, the majority of market participants will be looking for clues – such as improved production ramp-up, supply chain management, and margin expansion – to bolster confidence that improvements will continue through the second half and into 2023 in order to weather a looming economic downturn.
Tesla
Q2 Production and Deliveries: Tesla posted a sequential decline in delivery volumes during the second quarter as expected due to the three-week COVID-induced lockdown at its critical Shanghai manufacturing plant earlier in the period. The EV market leader produced 258,580 vehicles (+25% y/y; -15% q/q) in the second quarter and delivered 254,695 vehicles (+27% y/y; -18% q/q). The results “snapped a two-year streak of quarter-on-quarter gains”, while also falling short of consensus estimates on deliveries of about 261,000 vehicles (+30% y/y; -16% q/q), which had already been previously adjusted downwards from 279,000 vehicles (+39% y/y; -10% q/q).
FY 2022 guidance and near-term expectations: Although the second quarter delivery and production results drew focus on the extent of impact endured by Tesla during the three-week production halt in April at its Shanghai plant, it also brought to light again the EV titan’s ability in ramping up productions at unprecedented speeds. The EV maker’s Shanghai facility had been “producing vehicles at a rate of 17,000 units a week since the middle part of June”, which corroborates its statement that “June 2022 was the highest vehicle production month in Tesla’s history”. Specifically, Tesla’s shipments from its Shanghai facility surged 145% m/m in June, with more than 77,900 vehicles delivered to local Chinese buyers and close to 1,000 units exported abroad according to the CPCA.
The efforts also bolster Tesla’s aspirations to produce close to 1.5 million vehicles (vs. consensus estimate ~1.3 million to 1.4 million range) by the end of the year as guided by Musk during the first quarter earnings call. The EV titan has produced about 563,987 vehicles this year, with close to 565,000 vehicles delivered. This requires production of more than 936,000 vehicles over the next six months in order to achieve its target, implying a weekly production run-rate requirement of about 35,603 vehicles on average.
While July volumes from Shanghai might be muted again ahead of scheduled expansion works that are expected to last until the first week of August, the efforts aim to expand the facility’s output to 22,000 vehicles per week once the upgrades are complete. This would mark a strategic catch-up on plans to produce “8,000 Model 3s and 14,000 Model Ys per week” in Shanghai, which were originally intended for mid-May if it were not for COVID-related disruptions. At this production run-rate through the end of the year, Tesla’s Shanghai manufacturing plant is also expected to contribute an additional 458,860 vehicles (i.e. approx. 22 weeks x 22,000 vehicles weekly production run-rate) towards the company-wide production target for the year. Paired with annual production capacity from Tesla’s existing Fremont facility (approx. 600,000 vehicles per year), as well as continued ramp up at its new Berlin and Austin facilities, the EV maker remains on a positive track towards its production goal of 1.5 million units by the end of the year.
Fundamental and valuation forecast: Similar to expectations for the broader automotive industry, Tesla will likely reaffirm its previous production and revenue growth guidance for the year. We forecast a back-end loaded year for Tesla, as Shanghai gets back up to speed, and Berlin and Austin continue to improve on ramping up productions. Pricing gains will alleviate some of the pressure on near-term auto margins induced by higher input costs, as well as ramp-up costs related to the new manufacturing facilities as expected. Tesla’s re-introduction of the “Enhanced Autopilot” add-on option in the U.S. at $6,000, which essentially comes at zero marginal cost to the company, will also help cushion near-term pressures on profit margins and compensate for any potential slowdown to the $12,000 Full Self Driving (“FSD”) add-on option.
We expect deliveries to land between 1.4 million to 1.5 million vehicles in the current year. Paired with expectations for Tesla’s ongoing pricing gains resulting from recent price hikes and relentless demand, we are forecasting total revenues of $88.1 billion (+64% y/y) by the end of the year. While auto gross margins (ex-credits) are expected to dip from more than 30% in the first quarter to the 25% range in the second quarter, the above-mentioned improvements to Tesla’s global production ramp-up and higher-margin software sales are expected to caress the figure back towards 30% by the end of the year. However, we continue to caution downside risks pertaining to China’s fluid COVID situation, especially given the country’s unwavering compliance to stringent measures against the virus which could inflict further disruptions to Tesla’s business that are outside of its control.
We are maintaining our price target of $1,100 on the stock, which would represent upside potential of more than 55% based on the last traded price of $703.03 on July 11th. The expectation equally weighs valuations from 7x EV/’25 sales (lower range of 7x to 18x NTM EV/sales observed in the past 12 months) and 54x exit EV/EBITDA (average of 30x to 80x NTM EV/EBITDA range observed in the past 12 months) combined with a 10.7% WACC. The assumptions applied consider Tesla’s persistent push into dominating global EV sales over coming years, as well as its unmatched manufacturing capabilities and continued leadership in connected-vehicle software development, which is set to be a core driver of sustained margin expansion through the longer-term to support its valuation premium against peers.
Tesla Financial Forecast (Author)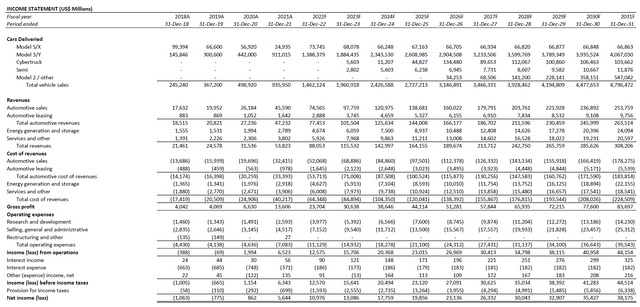
Tesla_-_Forecasted_Financial_Information.pdf
Rivian
Q2 Production and Deliveries: Rivian produced 4,401 vehicles (+72% m/m) and delivered 4,467 vehicles (+264% m/m) in the second quarter, representing continued improvements in ramping up productions as we had previously expected. The results beat the average consensus estimate on deliveries of 3,500 vehicles, bolstering confidence that the EV upstart’s reaffirmed guidance to produce 25,000 vehicles by the end of the year will be reached.
FY 2022 guidance and near-term expectations: Rivian had previously disclosed during its first quarter earnings call that approximately 1,400 vehicles were produced between April 1st and May 9th (i.e. approx. 5,000 vehicles produced since inception as of May 9th, less 1Q22 and 4Q21 production volumes). This represented a weekly production run-rate of about 280 vehicles per week at the time, which has since improved to an average weekly production run-rate of about 340 vehicles per week by the end of the quarter, and suggests an even higher weekly production run-rate of more than 370 vehicles per week in the days leading up to period end.
Continued acceleration of Rivian’s production efforts, paired with its reiterated production guidance of 25,000 vehicles for the year also corroborates a back-end weighted year for the EV upstart. With a production requirement of more than 18,000 vehicles over the next six months to meet its target, Rivian will need to ramp its manufacturing run-rate up to about 687 vehicles per week. Considering the wide production gap that needs to be narrowed still, Rivian’s planned expansion of its annual capacity with the addition of a second shift will be a critical catalyst.
However, the fluid situation over ongoing supply shortages across the automotive sector will remain a prominent downside risk for Rivian. In 4Q21 and 1Q22, Rivian’s production volumes have been largely a “function of supply availability” rather than its production capacity at the Normal facility as evidence by repeated delays to its start of productions timeline. The situation was likely exacerbated by the difficulties in ramping up productions on three models at the same time.
Recent speculation for a planned headcount reduction in non-manufacturing roles also draws concerns that the company may have expanded too fast over the past year to support productions that did not ramp-up nearly as fast as initially expected. While the company’s potential plans on eliminating duplicate functions could be just a pre-emptive decision to insulate against near-term macroeconomic uncertainties and spur greater operational efficiency to aid margin expansion, it could also imply slower-than-expected growth in the near-term, which makes another downside risk to watch for over coming months.
Fundamental and valuation forecast: Assuming Rivian will double its current production run-rate with an additional shift coming online sometime in the current quarter, and maintain its ongoing success in navigating through unprecedented automotive supply chain bottlenecks that are now seeing signs of gradual easing, we remain positive that it will meet its production target of 25,000 vehicles by the end of 2022. Our forecast projects end-of-year deliveries to total 23,334 units, which is consistent with Rivian’s improving production-delivery ratio in recent quarters as supply chain and logistics constraints gradually ease. This is expected to generate consolidated revenues of about $1.9 billion by the end of the year, considering a higher sales mix contribution from its retail consumer offerings (i.e. R1T and R1S sales) over its commercial offerings (i.e. Amazon delivery vans).
On the valuations front, the Rivian stock has dipped below $40 as we had previously expected given its decision to increase prices earlier this year foreshadowed heavier-than-expected input cost pressures, while investors’ confidence in the consumer sector also pulled back amidst the uncertain global economic growth outlook. With investors still looking for signs of consistent and sustained improvements to Rivian’s production ramp-up in the near-term, we are maintaining our near-term price target of $39 for the stock.
Rivian Financial Forecast (Author)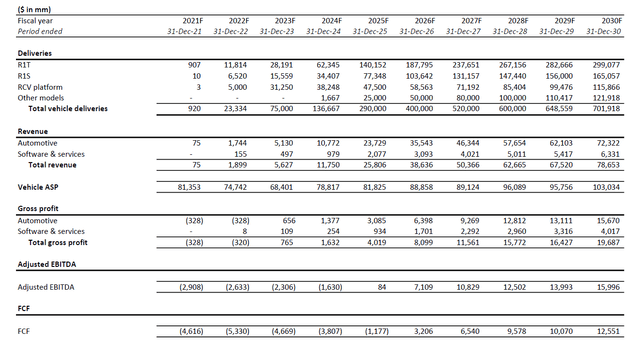
Rivian_-_Forecasted_Financial_Information.pdf
Lucid
FY 2022 guidance and near-term expectations: Consistent with historical practices, Lucid is not expected to announce its quarterly delivery and production results until second quarter earnings call, which is likely scheduled for early August based on previous disclosure timelines. Citing ongoing supply chain constraints as the key overhang to production ramp-up during the first quarter, Lucid’s near-term results – as in the case of Rivian – will likely continue to be a function of supply availability. Nonetheless, we expect production capacity to have improved over the past three months as it is likely that Lucid has completed deliveries of the Lucid Air Dream edition.
With the limited production of the Air Dream edition now out of the way, and ongoing supply shortages showing signs of improvement across the industry, productions of the Air Grand Touring is expected to have ramped favourably through the quarter. The upcoming debut of the newest add, Air Grand Touring Performance model, will also continue to corroborate Lucid’s premium brand identity with best-in-class technologies represented by industry-leading range and speed performance.
Considering production improvements observed across the EV peer group during the second quarter, we remain optimistic that Lucid has achieved similar results in ramping up productions. With Lucid’s deliveries totalling 360 vehicles in the first quarter, and another 300 vehicles in April alone, the EV maker is likely to have produced close to 700 or more vehicles in the first three months of the year.
Taking Rivian’s second quarter production improvements as a gauge, Lucid is likely to have produced approximately 1,200 vehicles during the second quarter. With similar production ramp-up expectations through a back-end weighted year for Lucid, its production volumes remain on a positive track towards the guided annual target of 12,000 vehicles to 14,000 vehicles, barring any new developments that could materially derail the gradual easing of auto industry supply constraints.
Positive commentary regarding its ongoing plant expansion at AMP-1 will also be a development in the right direction. Upon completion of the expansion expected in 2023, Lucid’s annual production capacity would increase from the current 34,000 vehicles to 90,000 vehicles at full ramp-up. Not only would this be critical to supporting on-time start of productions on Lucid’s Gravity SUV, but it will also be a key driver of margin expansion as the EV maker continues to scale up productions.
Fundamental and valuation forecast: Looking ahead, Lucid’s reiteration of its production guidance for the year will be a critical expectation from investors – any deviation from this already-downward-adjusted figure would be a negative shock to the stock’s near-term performance. If Lucid reaffirms its production guidance for the year, it would imply strengths in both supply chain management, as well as production ramp-up, which are key focus areas on EV start-ups this coming earnings season.
Considering the gradual, yet positive, improvements observed across the auto industry supply chain during the second quarter – particularly, in June – we are maintaining expectations for Lucid to achieve production volumes in the range of 12,000 to 13,000 vehicles by the end of the year. Consistent with expectations in our previous coverage, Lucid will likely experience a back-end loaded year:
The mediocre outlook expected in the first half of the year is expected to represent a shift in productions, rather than permanently lost units. Not only does Lucid’s manufacturing line have capacity to churn out 12,000 vehicles, the company’s growing talent base and the expectation for further easing of current supply chain bottlenecks will also accommodate production ramp up in the latter half to meet its set target.
We are also maintaining a near-term price target of $31 for the stock, which would represent upside potential of close to 70% based on the last traded share price of $18.53 on July 11th. Key valuation assumptions applied in our valuation analysis remains largely consistent with our previous coverage as Lucid’s operating environment and growth strategy has not materially changed. Despite a downward adjustment to near-term revenue cash flows due to temporary supply chain constraints, Lucid’s terminal growth outlook remains intact based on the foregoing analysis. Specifically, the ongoing build-out of Lucid’s global footprint, paired with the continued expansion of its product and technology roadmap is poised to advance its market share within the fast-growing luxury EV market in coming years, which further bolsters the stock’s valuation prospects ahead.
Lucid Financial Forecast (Author)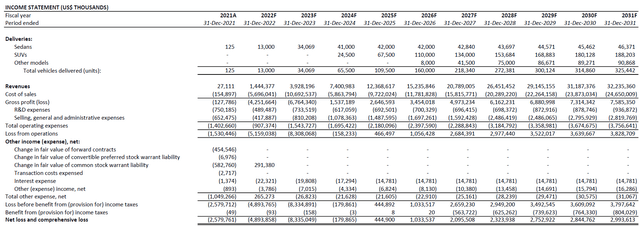
Lucid_-_Forecasted_Financial_Information.pdf
Polestar
Q2 Production and Deliveries: In Polestar’s last official sales update in mid-May, the Swedish EV maker announced record sales of 13,600 vehicles in the first four months of the year, while its order book grew by more than threefold over the same period last year to 23,000 reservations. At the said delivery run-rate, it would be on track towards delivering more than 40,000 vehicles per year, which would represent y/y growth of more than 40% from 29,000 vehicles delivered in the prior year.
But considering expectations for continued production ramp-up at shared manufacturing facilities with experienced parent companies Geely (OTCPK: GELYY) and Volvo (OTCPK:VOLAF / OTCPK:VLVLY / OTCPK:VOLVY), Polestar is progressing positively towards its delivery guidance of approximately 50,000 vehicles (+72% y/y) by the end of the year. Paired with easing of industry-wide supply chain constraints, especially with improvements to China’s COVID situation – in which Polestar had alluded to earlier this year for its slashed delivery guidance from 65,000 vehicles to 50,000 vehicles – the EV upstart could potentially outperform its target.
FY 2022 guidance and near-term expectations: By leveraging the manufacturing capabilities of parent companies Geely and Volvo, Polestar benefits from an “asset light” business strategy that is backed by experience in auto productions. Polestar’s ability to deliver 29,000 vehicles in 2021 and 13,600 vehicles in the first four months of the current year exceeds the 2022 – first full year production – guidance reported by peers Lucid and Rivian, underscoring the Volvo- and Geely-backed EV upstart’s asset light advantage.
With the Polestar 2 Electric Sedan already selling at a rapid take rate across major EV markets spanning Europe, Asia Pacific and the U.S., the EV maker’s continued roll-out of new planned models and expansion of its global footprint will remain positive catalysts for the stock this year. At Polestar’s upcoming inaugural earnings call, commentary over its upcoming launch of the Polestar 3 SUV expected in October, continued progression on its global expansion efforts, as well as delivery progress on its multi-year deal with Hertz (HTZ) will be key focus areas. Positive developments in related areas will bolster investors’ confidence in the stock’s valuation prospects, as they imply continued market share expansion and progression towards its ultimate sales target of more than 290,000 vehicles by mid-decade.
Fundamental and valuation forecast: Polestar’s post-close market valuation has been rangebound at the $20 billion range, with almost no premium to its implied enterprise value pertaining to the reverse merger with the Gores Guggenheim SPAC. The stock is now trading at an EV/FY’23 sales ratio of 3.1x, which is a discount to its EV peers with similar growth profiles and geographical reach.
We remain optimistic on our $18 near-term price target for the Polestar stock, which would represent upside potential of more than 80% based on the last traded share price of $9.95 on July 11th. The valuation outlook considers Polestar’s market discount to peers with similar growth profiles, as well as its nominal share float. Specifically, Polestar’s lack of a share float (potentially < 6%) will heighten the frequency of a demand-driven spike ahead of near-term catalysts, such as new vehicle launches and achievement of fundamental growth milestones (e.g. achieving/outperforming guidance, positive progress on global expansion plans, etc.) later in the year.
Polestar Financial Forecast (Author)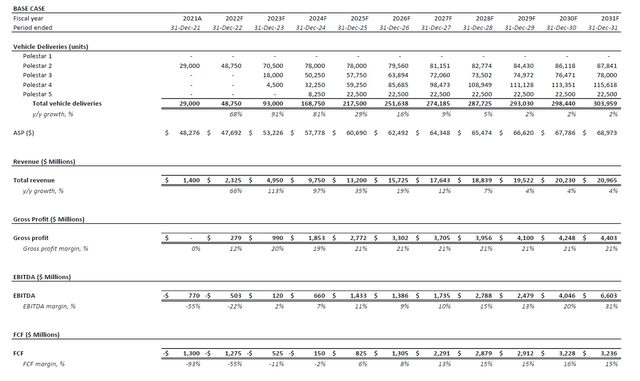
Polestar_-_Forecasted_Financial_Information.pdf
NIO
Q2 Production and Deliveries: NIO delivered 25,059 vehicles in the second quarter (+14% y/y; -3% q/q), underscoring reaccelerated growth as China re-emerges from the worst of supply and logistics constraints following recent COVID restrictions. Similar to its American EV peers, NIO delivered record-setting volumes in June. Specifically, productions of the newest ET7 sedan, which began in March, grew by more than 40x from 163 units in the first quarter to 6,749 in the second quarter, which highlighted NIO’s strength in re-ramping productions following heightened supply chain bottlenecks.
FY 2022 guidance and near-term expectations: Looking ahead, NIO is expected to post an even stronger second half, with the introduction of a strong product pipeline that adds the newest ES7 SUV to its sales mix beginning August 2022, alongside updated 2022 ES8, ES6 and EC6 SUVs. Favourable policy support in China as mentioned in earlier sections will also be a boon to NIO’s operational performance in the second half of the year.
Key focus areas for NIO’s upcoming earnings call will likely include the start of productions and customer deliveries timeline for its ET5 sedan which was launched in December 2021, as well as further detail regarding its mass market brand. While NIO has not provided details on the market entry timeline for the ET5 as it did for the newest ES7 in its latest delivery update, we are expecting the second sedan model to hit the roads before the end of the year. This is consistent with the anticipated start of productions timeline at NIO’s NeoPark phase I production facility dedicated to the ET5, which is expected to come online in the third quarter.
Pertaining to NIO’s new mass market brand, which was first mentioned in August 2021, the Chinese EV maker confirmed that it has entered into a “strategic corporation agreement with Hefei on the second phase of vehicle production plant and the facilities for key components at NeoPark” in early May. However, specific details over the product pipeline and related pricing remain uncertain. To date, NIO has only disclosed that the new sub-brand will be a direct competition to Tesla’s best-selling Model 3 and Model Y in China, but at a 10% discount in the RMB 200,000 ($30,000) price range. Start of productions and customer deliveries on the sub-brand offerings are expected to begin in the second half of 2024. Considering the anticipated launch and production timeline is still about two years out, it is unlikely NIO will provide additional details at its upcoming earnings call, but it should be an item on the look-out at its annual NIO Day event at the end of the year where new products and technologies are usually showcased.
A recent bearish report against NIO may also draw analyst questions regarding the company’s revenue recognition methodology for its battery-as-a-service (“BaaS”) business, as well as requests for clarification on progress pertaining to the independent investigation into allegations made by short-seller Grizzly Research. However, we do not anticipate the related developments to result in a material change to NIO’s price performance in the near-term considering certain inconsistencies within the bearish report that has drawn multiple analyst scrutiny over its integrity. This is further corroborated by the stock’s resilience in recent weeks.
In addition, we continue to caution downside risks pertaining to China’s fluid COVID situation, as well as regulatory risks pertaining to U.S.-listed Chinese stocks. A recent accident involving a NIO vehicle during testing at its Shanghai office is likely expected to draw questions regarding the viability of the company’s advance driving and autonomous mobility technologies.
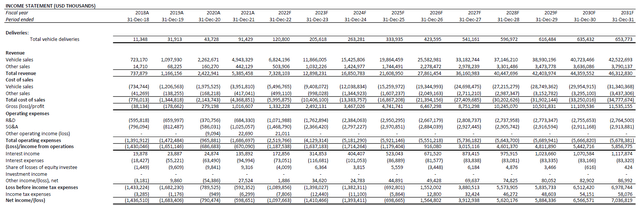
Fundamental and valuation forecast: With NIO’s exceptional June performance corroborating a back-end weighted year, we are forecasting annual volumes to exceed 120,000 vehicles by the end of the year. The assumption considers continued ramp-up at its existing joint venture production facility with JAC, which has an annual production capacity of 120,000 units to 240,000 units (based on maximum shifts of 4,000 work hours per year), as supply chain and logistics constraints in China show gradual easing. The addition of nominal volumes during early-stage ramp-up from the Phase I NeoPark production facility before the end of the year also corroborates the volume projections. This will accordingly translate to projected revenues of RMB 49.2 billion ($7.3 billion) by the end of the year, representing projected y/y growth of 36%.
Considering better-than-expected second quarter delivery volumes amid the early-period COVID slump, and gradual ramp up of productions through the remainder of the year as pandemic restrictions and related supply chain bottlenecks ease, we remain optimistic on our near-term price target of $27 for NIO’s stock. This would represent upside potential of more than 30% based on the stock’s last traded price of $20.57 on July 11th. The valuation forecast is derived based on a discounted cash flow analysis over a five-year discrete period in conjunction with our financial projections. The exit multiple of 25.8x applied on our valuation analysis reflects a perpetual growth rate of about 4%, which is consistent with the emerging EV sector’s high-growth, duration-characterized nature, as well as NIO’s status as one of China’s best-selling EV brands.
NIO Financial Forecast (RMB) (Author) NIO Financial Forecast (USD) (Author)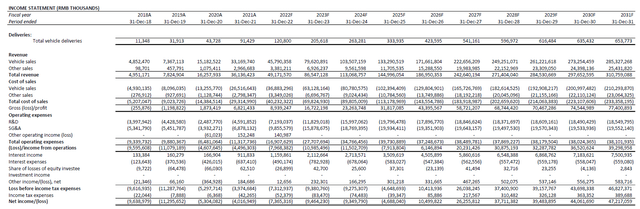
NIO_-_Forecasted_Financial_Information.pdf
XPeng
Q2 Production and Deliveries: Similar to NIO and Tesla, XPeng posted a resilient second quarter that underscored strength in ramping up productions after an early-period COVID slump in operations and sales across China. The EV maker delivered 34,422 vehicles (+98% y/y; +0% q/q) in the second quarter, with June volumes in the lead with triple digit y/y growth. Production of the P5 sedans are ramping up favourably since its introduction last year, with demand remaining robust for the best-selling P7 sedans. Meanwhile, production and delivery volumes on the G3/G3I SUVs steadied as XPeng shifts its sales mix focus on the higher-priced, higher-margin electric sedans.
FY 2022 guidance and near-term expectations: With increasing worries about a structural economic slowdown in Chinese consumption, investors will expect nothing less than strong growth guidance in Chinese EV makers to maintain confidence. And XPeng’s resilient second quarter results, paired with additional production capacity coming online in the second half of the year at its expanded Zhaoqing production facility will likely support the growth acceleration expected by investors.
Originally scheduled for completion by the end of the current year, XPeng’s phase two expansion in Zhaoqing would increase its current annual production capacity from 100,000 vehicles to 200,000 vehicles at full ramp-up. Investors are expecting phase two expansion to be completed on schedule to ensure timely production ramp-up through the start of 2023 to address XPeng’s growing order backlog. Any delays could push back its revenue recognition timeline and stall growth in the near-term.
Meanwhile, the anticipated start of reservations in August on the newest G9 SUV launching in September will be important for XPeng in the remainder of the year and through 2023. The newest five-seater, large-size SUV will broaden XPeng’s penetration into the premium EV market in China and bolster its market share in one of the country’s best-selling vehicle segments. Signs of pent-up demand for the vehicle after reservations begin later in the current quarter will help bolster the XPeng stock’s near-term performance, as it would imply resilience against a slowing domestic economy, with favourable margins to overcome impacts to free cash flow growth due to rising input costs.
In terms of downside risks, ongoing supply chain constraints across the broader automotive industry will remain an overhang on XPeng’s overseas expansion efforts. The Chinese EV maker has already suspended reservations on the P5 sedan in Europe, citing “global supply chain issues”, and the delivery timeline on existing P5 reservations also remains uncertain. The latest development is expected to partially counteract previous efforts made to bolster its presence in the rapidly expanding European EV market, which included the addition of two XPeng branded showrooms this year in Sweden and the Netherlands, as well as a collaboration with local auto retailer Emil Frey to broaden the Chinese EV maker’s reach in the region.
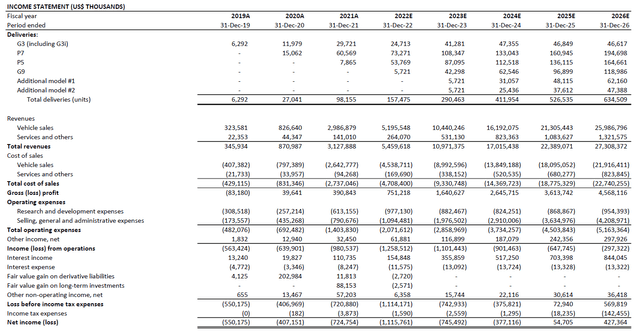
Fundamental and valuation forecast: Despite ongoing impacts from global supply chain bottlenecks, XPeng demand continues to outpace its production capacity. Considering the EV maker’s positive progression in ramping up productions and customer deliveries over the past two quarters under unprecedented industry challenges, we remain optimistic that XPeng’s annual delivery volumes can exceed 157,000 units (+60% y/y) by the end of the year, led by its best-selling higher-priced and higher-margin P5 and P7 sedans.
This is expected to drive revenues of RMB 36.6 billion by the end of the year, representing y/y growth of 75%. Revenue growth is expected to exceed volume growth considering the increasing mix of higher-priced P5 and P7 sedan sales, as well as the introduction of the higher-priced G9 SUV later in the year.
We are upgrading our 12-month price target for the XPeng stock to $36, which represents upside potential of more than 20% based on the last traded share price of $29.25 on July 11th. The revision accounts for XPeng’s proven outperformance in the first half of the year despite unprecedented production challenges, as well as the anticipation for greater-than-expected margin expansion this year supported by accelerating demand for the higher-priced P5 and P7 sedans.
XPeng Financial Forecast (RMB) (Author) XPeng Financial Forecast (USD) (Author)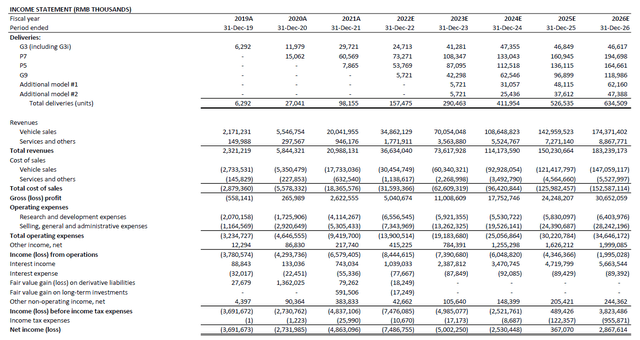
XPeng_-_Forecasted_Financial_Information.pdf
Final Thoughts
Production capabilities across EV OEMs will remain a key focus for investors during the upcoming earnings season, especially considering how they are mostly new start-ups with only Tesla having a competitive advantage in the two crucial areas required to outperform under the current macroeconomic environment: 1) securing supplies, and 2) scaling up productions to capacity. Other focus areas include developments over pricing power, supply chain management, top-line growth, as well as margin expansion to gauge longer-term performance prospects within the increasingly competitive EV landscape.
While growth opportunities remain robust in the EV sector, looming recession risks could serve as a near-term bump for OEMs. We are expecting greater focus across the EV industry on cost-savings initiatives in the near-term as an effort to preemptively insulate against impacts from a potential economic downturn. Meanwhile, continued production ramp-up, globalization and R&D efforts will remain in focus to ensure adequate capitalization of long-term growth opportunities ahead.


Be the first to comment