LemonTreeImages/iStock via Getty Images
Applied Materials (NASDAQ:AMAT) issued a press release on Oct. 7, 2022:
“The United States government announced new export regulations for U.S. semiconductor technology sold in China, including wafer fabrication equipment and related parts and services. Applied currently estimates that the new regulations will reduce its fourth quarter net sales by approximately $400 million, plus or minus $150 million.
The release stems from new sanctions by the U.S. government under new export controls announced on Oct. 7, 2022, semiconductors made with US technology. The relevant thresholds are as follows:
- Logic chips with non-planar transistor architectures (I.e., FinFET or GAAFET) of 16nm or 14nm, or below;
- DRAM memory chips of 18nm half-pitch or less;
- NAND flash memory chips with 128 layers or more.
The new sanctions also strictly limit exports to China of chip manufacturing tools and technology that Chinese companies could use to develop their own equipment. Moreover, Washington is barring US citizens or entities from working with Chinese chip producers except with specific approval.
A significant restriction, which I will discuss in detail in this article is that any U.S. citizen or green card holder working in China cannot work in the Chinese semiconductor industry or risk of losing American citizenship.
Exit Foreign Employees
According to The Wall Street Journal, U.S. chip-equipment suppliers are pulling out staff based at China’s leading memory-chip maker and pausing business activities there, according to people familiar with the matter, as they grapple with the impact of Commerce Department semiconductor export restrictions. The U.S. companies have reportedly stopped their support for equipment currently in place at Yangtze Memory (YMTC) and halted the installation of any new chip-production equipment.
According to a leaked internal email sent to staff but not denied:
“ASML US employees must refrain – either directly, or indirectly – from servicing, shipping or providing support to any customers in China until further notice, while ASML is actively assessing which particular fabs are affected by this regulation.”
This means that there may be no employees of the equipment companies servicing or providing support to customers. Akin to “defund the police,” these actions open the door for the possibility of Chinese companies to reverse engineer foreign equipment during this period. Chinese engineers can have free reins to detail any features of a piece of equipment they already don’t know during their maintenance programs.
How Extensive is China IP Theft?
The Center for Strategic and International Studies (“CSIS”), a bipartisan, nonprofit policy research organization, in an article entitled “Survey of Chinese Espionage in the United States Since 2000,” published a list of 160 publicly-reported instances of Chinese espionage directed at the United States since 2000. But an initial search of IP litigation identified more than 1,200 cases of U.S. entities against Chinese entities. So this is a serious and significant number.
Chinese Equipment Companies Coming on Strong
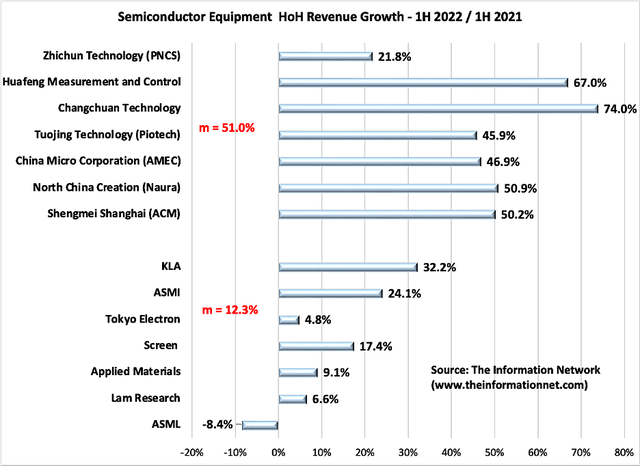
In Chart 1, I show that Chinese equipment suppliers’ revenues are growing significantly faster than non-Chinese companies, and this slower growth is reflected in imports as China moves to replace non-domestic semiconductor equipment with home-grown equipment, according to our report entitled “Mainland China’s Semiconductor and Equipment Markets: Analysis and Manufacturing Trends.”
Chart 1
Chart 1 above shows that the mean growth of Chinese equipment companies in 1H 2022 vs. 1H 2021 increased 51.0%. In contrast, the mean growth of non-Chinese companies (total global equipment only revenues) increased just 12.3%.
According to our report entitled “Global Semiconductor Equipment: Markets, Market Shares, Market Forecasts,” Applied Materials competes directly against the following companies in each of these sectors:
- ALD – Naura
- CMP Huahai Qingke Co
- Epitaxy – Naura
- PECVD – Piotech
- PVD – Naura
- RTP – Mattson (parent company Beijing E-Town)
- Dielectric Etch – AMEC
- Conductor Etch – Naura
While the Chinese companies have much smaller revenues than non-Chinese equipment companies, revenue growth is significantly greater.
Why AMAT Will Be Strongly Affected by China Sanctions
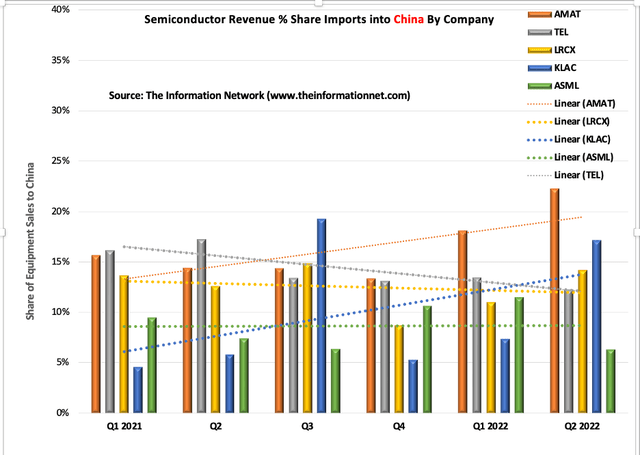
Chart 2 shows revenue growth from Q1 2021 through Q2 2022, and is actual revenue share of total imports into China from foreign equipment companies. With sanctions against ASML’s EUV lithography systems to China, revenue was weak in Q2 2022 as Chinese companies stockpiled DUV lithography systems before anticipated sanctions in the previous two quarters.
Chart 2 also shows that revenue from China for Tokyo Electron (OTCPK:TOELY) (“TEL”) dropped over the period, as evidenced from the trend line (grey dotted line). The trend lines of Lam Research (LRCX) shows a drop in revenues from China.
AMAT was strong, as evidenced by the orange dotted trendline, and the impact of China sanctions will greatly impact the company’s revenues. In addition to revenue, its larger base of different types of equipment in Chinese fabs place the company in the crosshairs of IP theft.
Chart 2
Investor takeaway
I’m already bearish on Applied Materials, as can be read in all of my Seeking Alpha articles on the company. An anticipated cyclical downturn in 2023, which I also discussed in several articles, adds a significant headwind following the current memory downturn.
AMAT has been underperforming competitors even before China sanctions. As shown above in Chart 1, in 1H 2022 compared to 1H 2021, AMAT grew 9.1% HoH, which is below the mean of 12.3%. KLA (KLAC) exhibited the strongest HoH growth of 32.2%.
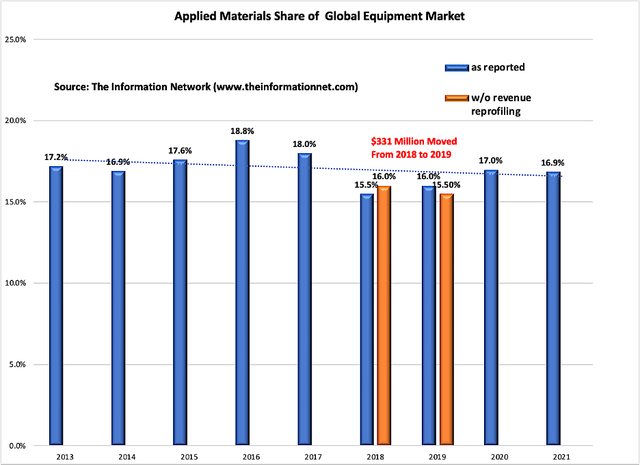
Not only has AMAT underperformed in 1H 2022, it has been underperforming since 2013 when new management took control from the AMAT acquisition of VSEA. Chart 3 shows the downward trend line between 2013 and 2021, It also shows how AMAT moved $331 million from 2018 into 2019 to improve market share (orange bars).
Chart 3
Chart 4 shows share price % change of these four companies over the past one-year period. It shows AMAT’s share price is -43.47% for the period even lower than even the VanEck Semiconductor ETF (SMH) at -32.55%. KLAC outperformed the group, down 20.02%.
YCharts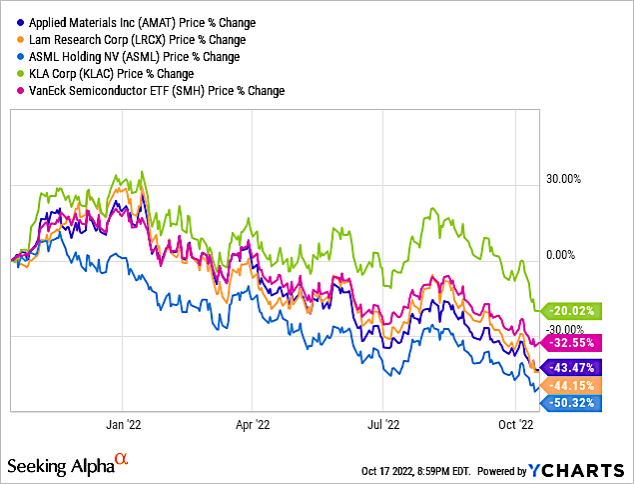
Chart 4
Chart 5 shows PE ratio for these four companies profiled. ASML has a significantly higher PE ratio of 24.91x compared to the other three companies.
YCharts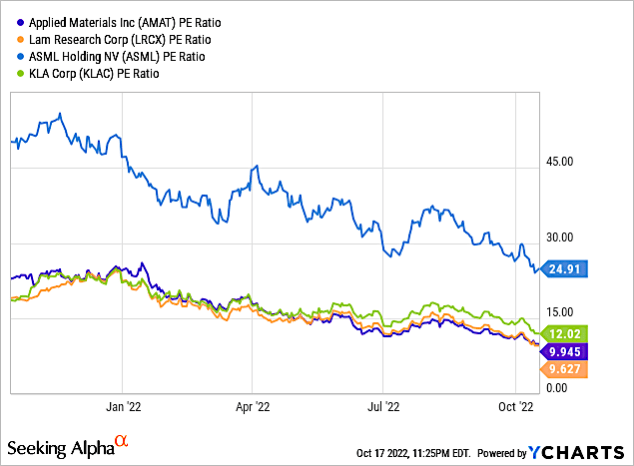
Chart 5
Significantly, any IP theft from reverse engineering can hobble AMAT even further, as competitors gain additional technical insight on AMAT’s equipment. As I’ve shown above IP theft by China is real and removing AMAT personnel from a fab using its state-of-the-art equipment will be disastrous, and the U.S. government needs to re-think this strategy.
Based on continued underperformance of AMAT, and now new China sanctions, I maintain a sell on this company.


Be the first to comment