Shutter2U/iStock via Getty Images
Ginkgo Bioworks Holdings (NYSE:DNA) is a Boston-based biotechnology company specializing in genetically adapting microbes for medical and industrial purposes. Leveraging the moderate success of its initial public offering in September 2021, Ginkgo has entered an ambitious but costly phase of stakeholder-facing long-term growth. The company is at the cutting edge of a young but rapidly expanding industry and is well-positioned to maintain its status as a market leader by innovating novel applications for its gene writing technology and microbial incubation techniques. Ginkgo is unique in that it is owned by Roche Holding AG, a holding entity that also owns Genentech, the revolutionary company that pioneered the commercial applications of cell programming. As an investment, Ginkgo Bioworks Holdings is a cheap, long-term buy opportunity with immense growth potential.
ycharts.com
Industry Analysis
According to estimates by McKinsey, by 2040, the biotechnology penetration across core markets will be worth nearly $4 trillion. There is immense potential for the applications of cell cultures across virtually every industry that dominates the global economy. The cell programming industry is driven by government interest, especially in the United States, which holds about 40% of the global biotech market share. Demand for cell programming biotech is growing rapidly in the Asia Pacific, specifically in India and China. The applications of cell programming are expanding the fastest in medicine and manufacturing. As of 2022, around 40% of all pharmaceuticals are developed with biotechnology. In the same vein, the manufacturing sector is increasingly relying on genetically programmed live cultures to produce rare industrial chemicals with high demand and short supply. Similarly, the cannabis industry is being revolutionized by cell programming biotech as chemicals like THC-V are being produced at scale with the help of genetically programmed yeast and E-Coli cells. With these novel applications, coupled with unmet demand, Ginkgo has an unprecedented opportunity to diversify itself into multiple high-growth industries.
COVID-19 Impact
Ginkgo used its specialized infrastructure to help research and develop treatments, cures, and solutions for COVID-19. The company’s COVID-19 response program is named “Concentric”, and involves partnerships with the government, labs, and private companies to aid in scaling up COVID-19 testing, optimizing vaccine development, and discovering therapeutics. The pandemic also pushed the company further in the direction of biosecurity, which has diverse and essential applications such as genomic surveillance and pandemic early warning systems. This expansion is reflected in Ginkgo’s Fiscal Year 2020 (FY20) portfolio of customers, which shows that, following the successful deployment of its biosecurity measures against COVID-19, the company gained a strong foothold in government defense and military projects.
Risks & Mitigants
The primary risk to Ginkgo is regulations. As the company forays into biosecurity and therapeutics, separate sets of complex regulations must be adhered to. Through its Concentric program, Ginkgo conducts nasal swab testing at a mass scale. In the process of testing samples, the company collects and analyzes genetic data. By building up an extensive genetic database, Ginkgo can deploy machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) to find new genetic insights that will yield innovative products and solutions. This automatically places the company in the crosshairs of regulators. There are concerns about genetic privacy. To address this risk, Ginkgo anonymizes all of the data it uses for research and product development, ensuring that the genetic data in its possession cannot be used to discriminate against people now or in the future.
Another risk to the company is legal liability. Ginkgo partners with healthcare, pharmaceutical, and biotech companies to develop medical therapeutics. Usually, this means that the company must seek FDA approval in order to market and sell its products. Getting FDA clearance could take over a decade and cost upwards of $1 billion. Ginkgo is structured in such a way that it does not market or sell products directly to consumers; therefore, the company is exempt from requiring costly regulatory approval. There is, however, a slight risk of ethical regulations impeding Ginkgo’s progress. There are religious and humanitarian objections to the company’s genetic programming and cultivation of mammalian cells. In the United States, moral objections to biotech are not present at the federal level. In fact, the National Institute of Health is actively funding Ginkgo to conduct research, which means that the risk of ethical and moral regulations is minimal.
Products Overview
Ginkgo was one of the first companies to offer a scalable market solution for cheap, effective, ethical insulin production. The company has since integrated horizontally and vertically to provide biotech solutions in virtually every industry that produces physical goods. Ginkgo gives its customers a state-of-the-art platform to program biological cells for customized medicine, cosmetics, agriculture, and manufacturing applications. As part of its post-IPO strategy, the company is focused on fleshing out its manufacturing, defense, food, and pharmaceutical verticals. Indicating its fervor for growth, in March 2022, Ginkgo acquired Swiss genetech company, FGen AG. FGen’s state-of-the-art screening technology will enable Ginkgo to widen the applications of its biotechnology by optimizing strain production and reducing expenses in the long run.
In FY20 -21, the company made strides in its food vertical, specifically in the lab-grown meat market. Ginkgo is strategically positioned to capitalize on every major worldwide obstacle, including pandemics, labor shortages, hunger, and climate change. Cultured meat, for example, is a young industry with a lot of funding from multilateral and government institutions. In the next century, synthetic meat is projected to replace a significant share of the global meat supply. By expanding into this niche industry and many others like it, Ginkgo is ensuring a steady supply of funding, tax breaks, and revenue in the far future. From an Environment, Social, and Governance perspective, the company is optimally structured and governed to deliver alpha gains over a multigenerational time horizon. This makes Ginkgo a suitable investment for pension funds, trust funds, sovereign funds, and inheritances, thus ensuring that the company’s market value will move in a positive, blue-chip direction over time.
Ginkgo has expressed interest in expanding into space travel. Long extraterrestrial journeys can be facilitated with the help of genetically programmed cells that produce oxygen, absorb greenhouse gasses, neutralize waste, and preserve food. This foray into the frontier of existential endeavors will mark the mature phase of the company’s operations. It also signifies the true potential for returns on investment in the long term. With an imaginative, ambitious, and forward-thinking management team, Ginkgo is well-positioned to achieve stellar growth, making it an increasingly attractive and profitable investment over time.
Financial Analysis
When Ginkgo was founded in 2009, most of the funding came from government grants, suggesting that the company was conceived to serve as part of permanent public infrastructure. This is a lucrative long-term opportunity, as government contracts are stable sources of revenue with the potential to reach a national or worldwide scale. As of FY21, the company’s revenue streams come from foundry payments, biosecurity, royalty payments, and equity in its subsidiaries and partners. Foundry revenue refers to grants and payments from partner companies for the purpose of developing custom products. Ginkgo has a growing list of partnerships and, in FY21, involved itself in 21 new programs, adding to a total of 61 active programs. In short, third parties contract and partner with Ginkgo so that they can use the company’s gene-writing platform to conduct research and development (R&D). In return for allowing partners to use its technology, Ginkgo receives foundry payments that cover operating expenses and provide liquidity. Once the end-products hit the market, Ginkgo receives a portion of the sale proceeds as royalty. This model of operation saves Ginkgo the expense and trouble of marketing its own products while also shielding the company from most regulations. With passive income from foundries and royalties, the company can focus on the technical side of things. In FY20, foundry revenue amounted to $59 million. By the first half of FY21 (H1-21), foundry revenue increased by $41 million year-on-year (y-o-y), in line with the increase in the number of active programs. Foundry revenue is inherently stable, low-cost, low-risk, and ensures long-term solvency.
investors.gingkobioworks.com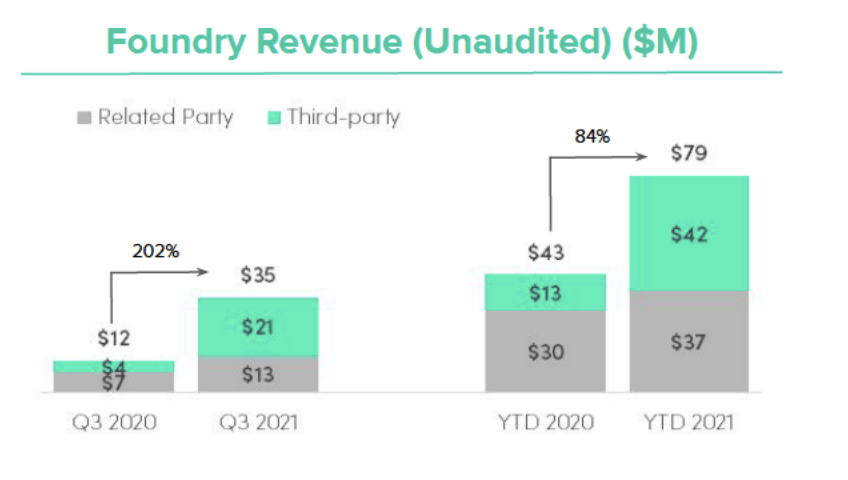
In FY20, the company earned $17 million from biosecurity operations, specifically through COVID-19 testing contracts with thousands of schools across the United States. While biosecurity revenue in the form of COVID-19 testing may have been one-off due to the pandemic, Ginkgo is establishing permanent biosecurity revenue pipelines by building early warning screening systems at major airports. To this end, in the first half of FY21 (H1-21), the company earned $44 million in biosecurity revenue, a massive increase from the previous year. As of FY22, Ginkgo is yet to receive any royalty revenue. However, the first program is expected to come to fruition sometime in H1-22. Due to the nature of this model, royalty revenue will grow at an exponential rate as the growing list of 61+ programs reach maturity. Long-term growth is predicated on developing new business relationships and expanding into new horizontals. This process will be costly, and given that Ginkgo is at a very early stage of operation, it will be a while before there are major advances in terms of profit. As more end-products hit the market and cell programming technology becomes cheaper, Ginkgo will be able to deliver positive earnings per share, which is sure to sway market valuation. The third fiscal quarter (Q3-21) results show that the company is on its way to rapidly achieving higher revenues with every quarter. In Q3-21, total revenue increased by 271% y-o-y to $165 million. Due to the costs of growth, the company is running a net loss of $232 million. The losses are driven mainly by a surge in expenses relating to biosecurity cost of sales, R&D, and administration. Expenses are expected to increase as more revenue pipelines are established and expanded.
Future Outlook & Final Thoughts
Due to the recency of Ginkgo’s IPO, it is too early to make a call regarding the company’s position on the stock market. From a value investment point of view, the company boasts strong fundamentals, competent management, private and government backing, and high industry demand. By acquiring specialized biotech companies, Ginkgo is exponentially growing its pool of data, technology, and talent, all while developing a de-risked and diversified portfolio of holdings. The company is highly attuned to ESG trends and is positioned to leverage the most pressing multilateral initiatives in the world. As an investment, Ginkgo is undervalued and sure to deliver significant returns in the long run. Investing in the company at this early stage is akin to buying shares in Apple in 1980 — that is to say that Ginkgo may very well be a once-in-a-lifetime investment that will hold its appeal across multiple generations.


Be the first to comment