sudok1/iStock via Getty Images
Thesis
Since my last coverage, BioVie’s (NASDAQ:BIVI) share price has moved up +100%, on increasing volume. Since my first coverage, the stock has moved up somewhat about than 200%. My view on BioVie has gone from seeing the initial potential but remaining skeptical, to very bullish in light of the Alzheimer’s disease data reported in September 2022. BioVie is at a pivotal time in its evolution, with data having been reported in both Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, coming out of Phase 2 trials, one of which was placebo-controlled. The company’s stock still seems to have a lot of potential runway.
Last week at the international Alzheimer’s conference in San Francisco, where most eyes were on Eisai (OTCPK:ESALY) and Anavex (AVXL), I believe it was BioVie that actually presented the best data.
During post-market trading on Monday December 5, 2023, BioVie announced positive data from its – fairly short – Phase 2 placebo-controlled Parkinson’s trial. The trial met its goals, and showed that NE3107 considerably improved motor control for patients who were on standard of care Levodopa. I believe this is big news for the Parkinson’s world.
On Tuesday December 6, 2023 during pre-market trading hours, BioVie issued yet another press release, announcing NE3107 drug’s ability to reverse Alzheimer’s patient’s biological clocks by 3.3 years over a treatment duration of 3 months. This is in addition to Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s data that were very strong, and with striking consistency. The efficacy signal seen in patient’ biological clocks was seen in 19 of 23 patients, and strongly outperformed the efficacy reported from a small 2019 trial that had shaken up the world of epigenetics quite a bit at the time. That Tuesday press release is very much consistent with the essence of my investment here, as I will explain below.
The drug is consistently found to be safe.
With a potentially pivotal Phase 3 trial in Alzheimer’s disease midway, BioVie may be furthest progressed in finding a disease-modifying solution to Alzheimer’s. That trial will read out before the end of the third quarter of 2023, which is less than ten months away. The ambition does not seem equal to that of an anti-amyloid drug, but rather stabilization or improvement of the memory-destroying disease with one drug, with an oral drug candidate that does not come with side effects.
There is global peak revenue potential of above $13 billion.
The Road To Solving Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s
Anti-Amyloid Therapies: Unsafe And Moderately Slowing Cognitive Decline
As I had mentioned in my article ‘Trading Ideas On The Upcoming CTAD 2022 Conference’, the past Alzheimer’s Conference has been one to remember. Trading has been volatile for most companies mentioned in that article. The traditional Alzheimer’s therapies focused primarily on the first hallmark of the disease, namely amyloid beta. For the first time in years, an anti-amyloid therapy actually works, full data is out, and details have now been published in the New England Journal of Medicine. Lecanemab showed 27% slowing of cognitive decline on CDR-sum of boxes, starting at 6 months.
Lecanemab cognition chart (New England Journal Of Medicine)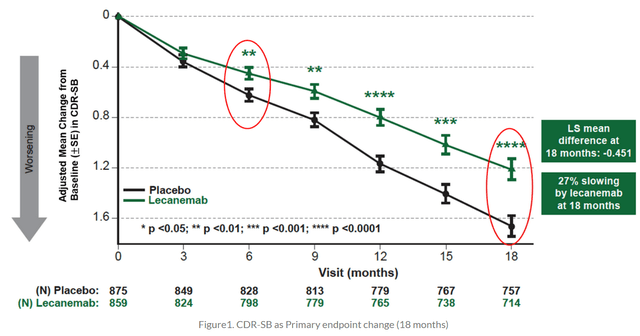
Slowing of cognitive decline on other measured rating scales was 26% on ADAS-Cog14 or a mean -1.44 point, 24% on ADCOMS or a mean -0.050 point, and 37% on ADCS-MCI-ADL or a mean – 2.0 point score. Lecanemab comes with the typical anti-amyloid therapy side effect, i.e. amyloid-related imaging abnormalities or ARIA. ARIA-E occurred in 12.5% of the Lecanemab group and 1.7% in the placebo group. Two patient deaths who claim to be related to Lecanemab have also been reported. ARIA is essentially inflammation resulting in brain edema or swelling. Those who have read me know that I believe that the best solutions in neurodegenerative diseases may come from second-generation anti-inflammatory drug candidates. This is where the science is at, and BioVie’s NE3107 lowers TNF-alpha in a non-immunosuppressant manner. Hence, I am taking a step back to cover how traditional TNF-inhibitors have changed the medical landscape.
TNF-inhibitors for bodily inflammatory conditions: the biggest drug franchise ever
TNF, often considered the master regulator of inflammation, is the first cytokine to appear after any injury or stress, with other pro-inflammatory cytokines to appear much later. Traditional non-selective TNF-inhibitors have revolutionized the treatment of inflammatory conditions of the body. Humira (adalimumab), Remicade (infliximab) and Enbrel (etanercept) are the most known ones. They have been approved for several conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis or ankylosing spondylitis. The development of Infliximab, the first TNF inhibitor to be approved, had however started in a small US biotechnology company.
TNF inhibitors’ biggest side effect is immunosuppression and hence a serious risk of infections such as tuberculosis or fungal infections like histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, and blastomycosis. TNF inhibitors are also related to demyelinating events. Myelin, a fatty tissue created by oligodendrocytes, a subset of immune cells of the central nervous system, provides the insulation for signal transmission across axons. It is also implicated in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. TNF-inhibitors have been tested for multiple sclerosis as well, a neurodegenerative disease, where they also appeared to lead to demyelination, probably through the immunosuppression.
It was AbbVie’s (ABBV) adalimumab or Humira that eventually grew into the best-selling drug of all time. By the end of its US patent life in 2024, Humira is expected to have led to $240 billion in sales revenue. And AbbVie is mapping the unmet medical needs in the inflammatory space and actively looking for replacements of Humira.
Although currently approved TNF inhibitors are not approved for diseases of the central nervous system and cannot pass the blood-brain-barrier, several retrospective studies in millions of patients have shown a remarkably reduced risk of Alzheimer’s for patients on traditional TNF inhibitors. The reduction in risk ranges from 30% to 70% compared with non-use of these drugs. That is actually the remarkably similar scientific basis for both BioVie and INmune Bio’s (INMB) drug candidates.
Inflammation And Systems Dysregulation In Neurodegenerative Diseases
I believe that probably the biggest unmet medical needs in the inflammatory space may be found in potential treatments of neurodegenerative diseases. Neuroinflammation, insulin resistance and oxidative stress are common features in the major neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Parkinson’s Disease (PD), frontotemporal lobar dementia, and ALS. The title of this chapter and the sentence above are taken from a recent press release by BioVie.
Slide on similarities between neurodegenerative diseases (BioVie R&D webinar 2021)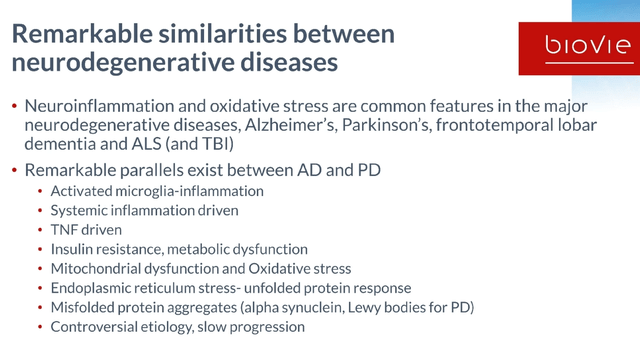
There is a common hallmark across all neurodegenerative diseases, and that it is chronic low-grade inflammation driven by chronic immune activation in the brain, particularly driven by the most abundant immune cells of the brain, microglia and astrocytes. Those cells constantly survey, clean up debris, prune unnecessary connections, and in so doing sculpt the brain…if they are working as they should.
Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s are characterized by systems dysregulation driven by chronic low-grade inflammation. That inflammation seems to be initially triggered by aging, the cumulation of inflammatory stressors throughout life, and may be different for each individual. Terms often referred to are ‘inflammaging‘ or ‘immunosenescence‘.
Slide on inflammation driving systems dysregulation (BioVie R&D webinar 2021)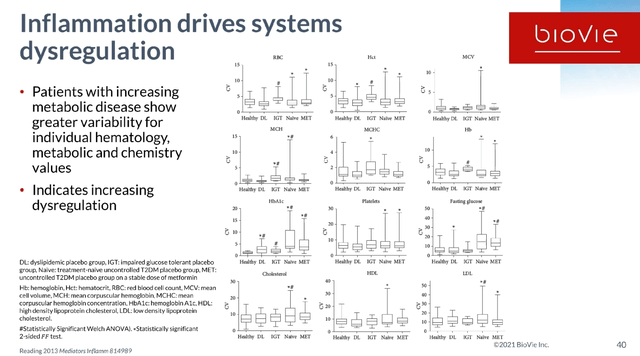
That means anti-inflammatory agents may have an effect across neurodegenerative diseases, which why some of the companies I have covered pursue their immune-modulating drug candidates in more than one neurodegenerative indication. NE3107’s success in both Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s makes sense from that perspective. Additionally, the Levodopa-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease patients is driven by inflammation. And anti-amyloid therapies come with inflammatory ARIA as a side effect, insofar as combination therapies could one day be considered, as suggested by the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Association after the news on Lecanemab.
NE3107 as a novel safe, brain-penetrant, efficacious, not immunosuppressant anti-inflammatory agent
Introduction
BioVie’s NE3107 is a non-immunosuppressant anti-inflammatory insulin-sensitizer. Prior to its Phase 3 trial in Alzheimer’s, NE3107 had proven to be safe and well tolerated in 178 subjects, with a total experience of 18.9 years of drug exposure. Preclinical studies showed that NE3107 is a brain-penetrant modulator of TNFa production, through its ability to modulate the activation of the Extracellular Regulated Kinase (ERK) and Nuclear Factor kappa B (NFkB), but not affecting their homeostatic functions. radicals. Selective NF-kB and ERK inhibition is necessary, as NF-kB and ERK have critical homeostatic functions, the inhibition of which could lead to neuronal loss or insulin signaling, among others.
NE3107 dual mechanism of action (BioVie Corporate Presentation)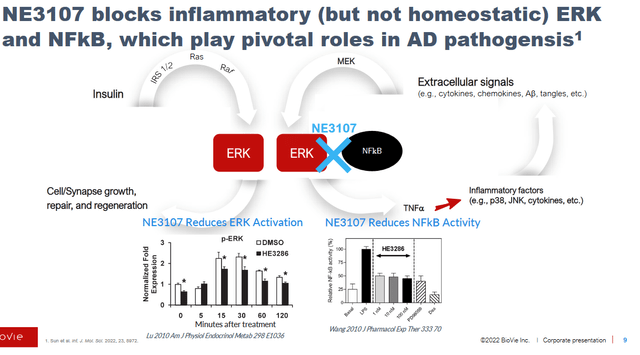
The safety and prior testing has provided a detailed rationale for BioVie to proceed to a Phase 3 trial in Alzheimer’s. NE3107 has also been shown to have neuroprotective properties in previous trials.
NE3107 slide on neuroprotective properties (BioVie Corporate Presentation)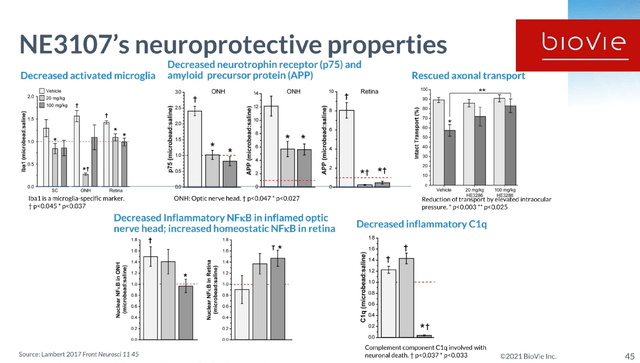
NE3107 seems to come with all the requirements that an anti-inflammatory agent for diseases of the central nervous system should have. It is safe, brain-penetrant, reduces inflammation, modulates insulin-signaling gone awry, and is not immunosuppressant. And the field is looking at this, as was shown on May 19, 2021, when neurologist Alan Mazurek of Mount Sinai was quoted saying the following during a B. Riley Securities interview [own underlining]:
I would like to talk specifically about some of the immune drugs, because we’ve touched on that. We touched on tumor necrosis factor, we touched on NF-kB, and we didn’t mention it, but I’ll mention it now, extracellular signal regulated kinase or ERK. These are all very significant regulators of cell function, myosis, mitosis as well as microglial function. And, clearly, if we could come up with medications that could target any one of these or perhaps all of these, that could be quite exciting. Looking at it, I saw there was a drug by Neurmedix called NE3107, which had just been authorized to form a pivotal Phase 3 Alzheimer’s disease trial because it does affect all three mechanisms of action that I had mentioned: TNF, NF-kB and ERK. And what was exciting about some of the early studies, the Phase 2 studies, is that there was no significant toxicity, it was not immunosuppressive and because it was an oral drug, again, it was very easy to utilize. So, I’m trying to look at the big picture and I appreciate what Dr. Sadowski is saying about all of the anti-amyloid therapies that we’ve tried but I think we have to turn the aircraft carrier a little bit more away from the amyloid venue because otherwise we are going to be continually using other medications to treat some of the harms we’ve caused.
I am of the opinion that NE3107 may not be the only drug in the running here. Cassava Sciences’ (SAVA) simufilam reduces neuroinflammation through the TLR4-receptor, which itself is linked to transcription factor NF-kB and microglial polarization. INmune Bio’s Xpro is a non-immunosuppressant selective TNF inhibitor which has shown preclinical potential and remarkable success in a Phase I study. None of these seem to come with side effects. I have mentioned these other drug candidates here, because the consistent success from these drug candidates is what compels me from an investing point of view. That consistency could be seen as a confirmation that a potentially much stronger effect than that seen in an exceptionally successful anti-amyloid drug candidate such as Lecanemab could be in the making, without side effects.
NE3107 second mechanism of action: insulin resistance
Alzheimer’s is often called type 3 diabetes or ‘diabetes of the brain‘, as the metabolic changes and insulin resistance seen in the brain of Alzheimer’s patients, particularly the lack of correct insulin signaling, are similar to those seen in diabetic patients. Over 80% of Alzheimer’s patients also have type 2 diabetes and people who have type 2 diabetes may be up to 60 percent more likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease or another type of dementia.
BioVie considers that NE3107 is the only molecule that is pursuing both neuroinflammation and insulin resistance. Next to its action on TNF, it also modulates insulin-signaling, which may be an equally important additional mechanism of action.
Insulin is considered the master regulator of glucose, lipid and protein metabolism. The brain is in constant need of glucose and lipids, and many neurodegenerative diseases are often seen as protein misfolding diseases. Particularly for Alzheimer’s, APOE4 as biggest genetic risk factor drives inflammation through lipid transport gone awry.
Normalizing Systems Dysregulation
Though the extent of patients’ biological clock reversal is a different story altogether, I believe the recent announcement of NE3107’s potential to reverse Alzheimer’s patients’ biological clocks was in the making for those watching closely. BioVie’s May 19, 2021 R&D day was considered to be of the utmost importance by BioVie’s C. Reading, PhD. This was his introduction to the below slide (min. 40):
And Cuong [CEO] told you, you only had to remember a couple of his slides, but I want you to remember this one because this is the one that I think really tells us that we got a good chance in having a major impact in Alzheimer’s disease.
When we did a study in type 2 diabetes, we were able to show this abnormal data distribution in the placebo group. At the end of the study we could demonstrate that they all had very dysregulated data distributions for all of these parameters listed.
But we found that subjects that had been treated with NE3107 for 84 days now had normalized their data sets. There were placebo patients where the data was statistically random and we were able to show that those data, in the treatment arm, those data became normalized. So we believe that this is the basis, inflammation-driven systems dysregulation, and it’s impacting all of these parameters.
NE3107 Decreases Systems Dysregulation (BioVie Corporate Presentation)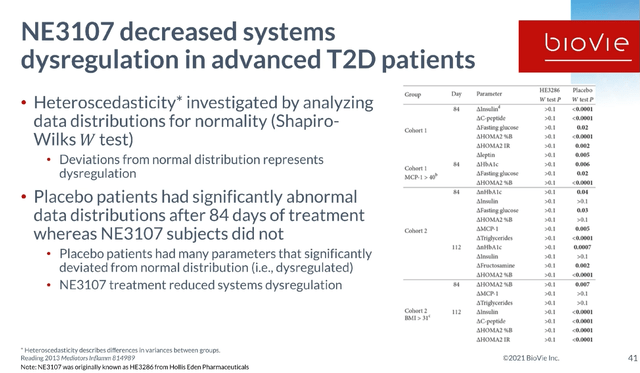
As scientific congruence is essential to investments for me, I add that a very similar development had been remarked during INmune Bio’s first webinar on Phase 1 study results. INMB’s CEO had commented: “[…] and to me this is what normalizing looks like. In other words we took the dysfunctional chaotic innate immune system and brought it back to normal. So, time will tell if that interpretation is right but we believe the future is bright.“ And that data came from a study in Alzheimer’s patients.
NE3107 in Alzheimer’s Disease – Phase 3 Trial With Considerable Potential Midway
Data Reported Prior to CTAD 2022
BioVie had on September 7, 2022 announced that, in an open label Phase 2 study, NE3107 treatment saw 82% of 17 patients with MMSE >=20 experience a 2.6 point decrease in ADAS-Cog12 (p=0.0046). A similar pattern of improvement was observed using the QDRS, a rating scale to assess cognition and function, scored from 0 (normal) to 3 (severe impairment), where 71% of 17 MCI/mild AD patients improved with a mean change of -1.35 (p=.0051). NE3107 was also associated with improvements in the patients’ daily abilities and overall sense of well-being as reported by the clinical, families and patients on the basis of the Global Rating of Change rating scale, with p-values ranging in between p<0.0001 and p<0.05.
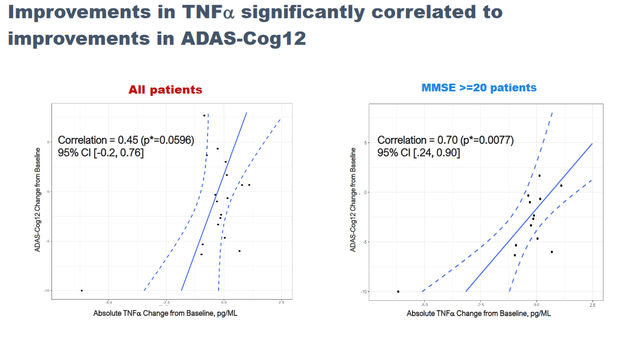
NE3107 treatment saw a significant correlation between reductions in the inflammatory marker TNFa and improvements in cognition.
That initial reporting further saw reduced CSF p-tau levels, improvements in blood flow, a lower ratio of p-tau to Aβ42predictive of amyloid burden, reduction in hyperactivation of the hippocampus and increased levels of glutathione as a master regulator of oxidative stress.
No drug related adverse events have been reported.
Many of these initial findings have been covered more extensively in my earlier coverage, so I will limit it here to some fundamental slides.
NE3107 Phase 2 Adas-Cog12 data (September 7 Reporting – Corporate Website) Cognitive Correlations With TNF Reduction (BioVie Corporate Presentation)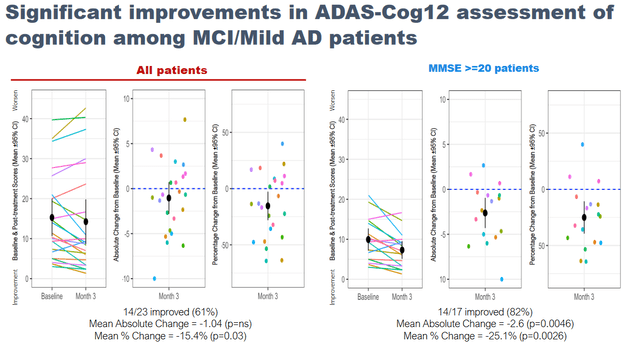
BioVie reported quite some additional information during the Alzheimer’s conference, which I will try to summarize below. The full data can be found here.
Full rating scales data presented at CTAD
As a reminder, Alzheimer’s disease is marked by consistent decline in cognition, which is why the 27% slowing of cognitive decline shown by Eisai’s Lecanemab in a Phase 3 trial was hailed worldwide as a medical breakthrough.
Possibly to avoid discussion as to potential placebo effects coming out of its Phase 2 data, BioVie did a considerable number of cognition and function tests on its Phase 2 patients. At last week’s CTAD conference, all of these data have been presented. On multiple standard rating scales, BioVie has now shown that NE3107 has positive effects on cognition and function in Alzheimer’s patients.
Slide On Rating Scales Results CTAD 2022 (CTAD 2022 Presentation – Corporate Website)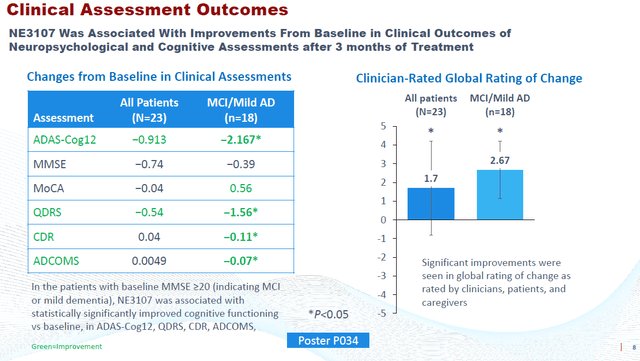
Given the extent of the data reported, I chose to only include part of it below.
First Slide Cognition Scales (CTAD 2022 Presentation) Second Slide Cognition and Function Scales (CTAD 2022 Presentation – Corporate Website)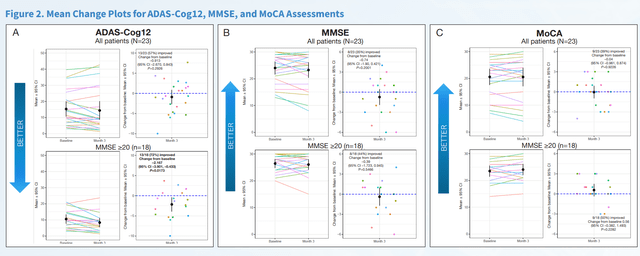
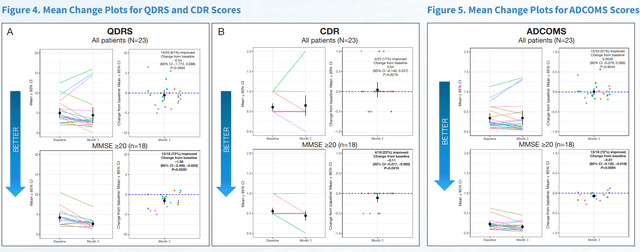
The 2.2 point improvement on ADAS-Cog12 equates to a 121.1% (p=0.0079) reversal of cognitive decline, if one wants to compare to Lecanemab’s results. Among only responders, the improvement was 3.7 points equating to 36.2% compared to baseline.
NE3107 treatment saw an improvement of 0.11 on the Clinical Dementia Rating scale or CDR, equating to 19.4% change from baseline. As a reminder, Lecanemab’s results came from the CDR-Sum of Boxes rating scale.
And yet another improvement of 0.07 points was noted on the Alzheimer’s Disease Composite Score or ADCOMS.
The consistency across these data is striking. It is hard to imagine Alzheimer’s patients, on a physical path of neurodegeneration and concomitant continuous cognitive decline, performing like this on different rating scales, just because they believe they are being given a good drug. Disease stabilization by the use of one treatment would be excellent. From what I am seeing, NE3107 may even have more in store, on the basis of the consistency across these rating scales alone. But BioVie also presented corroborative biomarker and neuroimaging data.
Biomarker data presented at CTAD
At CTAD, the final biomarker data confirmed that treatment with NE3107 was associated with trending improvements in plasma TNF-α, brain glutathione levels, lower CSF p-tau levels, and p-tau:Aβ42 ratios. I considered this to be the most interesting slide of the poster on this topic.
Biomarker data Phase 2 AD – CTAD 2022 (Corporate Website)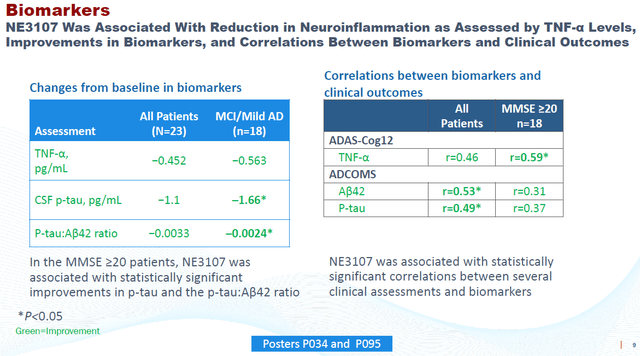
Neuroimaging data presented at CTAD
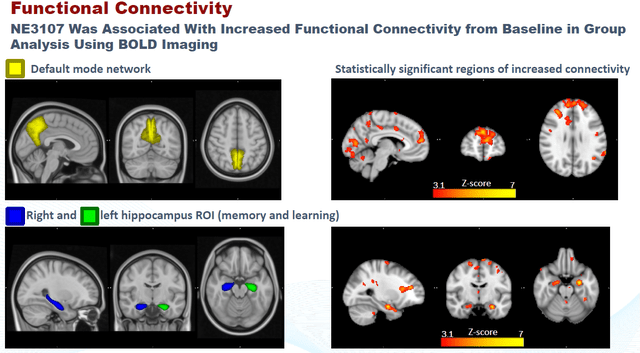
Finally, BioVie released neuroimaging data that again was consistent with the above. Functional MRI data had been submitted to different clinicians on a blinded basis, to analyze oxidative stress on the basis of glutathione levels and functional connectivity. The slides below are what I considered most interesting from the presentation on this topic.
NE3107 Correlation to Reduced Oxidative Stress (CTAD 2022 – Corporate Website) NE3107 Correlation To Brain Functional Connectivity (CTAD 2022 – Corporate Presentation) Neuroimaging Conclusion (CTAD 2022 – Corporate Website)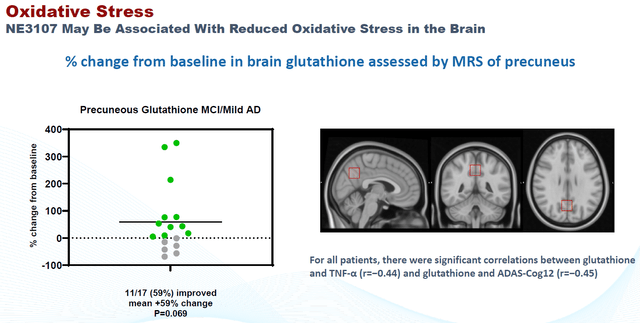
Phase 3 trial in Alzheimer’s Midway
BioVie’s Phase 3 trial in Alzheimer’s is a potentially pivotal randomized, double blind, placebo controlled study, which had started enrolling in August 2021. The trial’s initial patient number was 316. The FDA’s Data Safety Monitoring Board could see the data unblinded, and could advise BioVie to enroll about 80 additional patients to enhance the probability of achieving statistical significance.
BioVie has announced on November 29, 2022 that due to the fast pace of enrollment over the past few months, the company would not await the DSMB’s pre-specified interim data analysis, and would enroll the entire 400 patients. The company now expect the trial to be fully enrolled in two months, with topline results being anticipated before the end of 3Q2023.
NE3107 for Parkinson’s disease
Introduction
I have set out the basis of NE3107 as an anti-inflammatory agent in neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson’s disease.
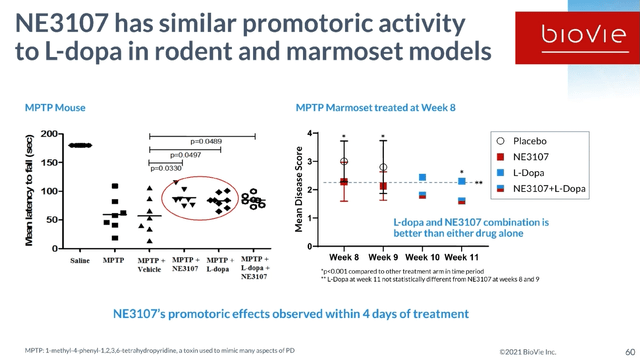
The standard of care in Parkinson’s disease is levodopa. The problem with levodopa, however, is that it induces dyskinesia, which is referred to as Levodopa-induced dyskinesia or LID. Dyskinesia, which is not a symptom of Parkinson’s disease itself, entails involuntary, erratic, writhing movements of the face, arms, legs or trunk. LID is being driven by inflammation. NE3107’s potential in Parkinson’s is the improvement of levodopa’s effect by reducing the inflammation-driven neurodegeneration, as well as the levodopa-induced dyskinesia. In both rodent and monkey models, NE3107 has promoted an equally promotoric activity as levodopa, with the combination of both being better than either drug alone. NE3107 has also been shown to preserve neurons and to promote neuroregeneration in a monkey model.
NE3107 Preclinical Results Parkinson’s Slide 1 (BioVie R&D Webinar 2021) NE3107 Preclinical Results Parkinson’s Slide 2 (R&D Webinar 2021)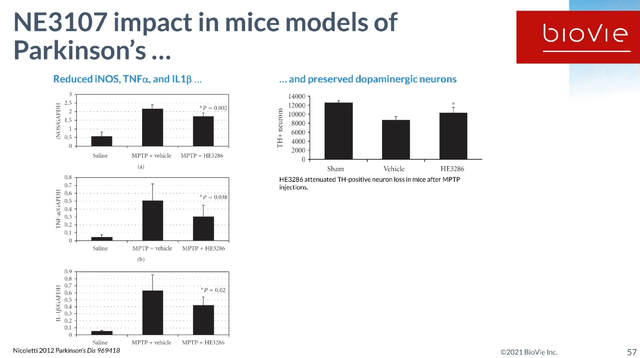
For this reason, BioVie had started a randomized placebo-controlled Phase 2 trial in Parkinson’s disease, where patients would combine levodopa with NE3107. In that regard, one should know that levodopa is a symptomatic treatment that works for a limited amount of time. Peak plasma concentrations are reached after an hour, and remain elevated for 4 to 6 hours thereafter. ‘Off-time‘ is referred to as the time when levodopa’s effect has waned, and symptoms such as tremor and rigidity re-appear. The trial’s objective was to assess drug-drug interaction, and motoric function of levodopa+NE3107 compared to levodopa alone over the course of levodopa’s effect. Motoric function is assessed by Part III of the UPDRS rating scale. Here is a chart showing what normal progression on Part III of UPDRS is in patients that are not treated with levodopa, versus those that are.
Normal progression on UPDRS Part III (PubMed: Progression of MDS‐UPDRS Scores Over Five Years in De Novo Parkinson Disease from the Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative Cohort)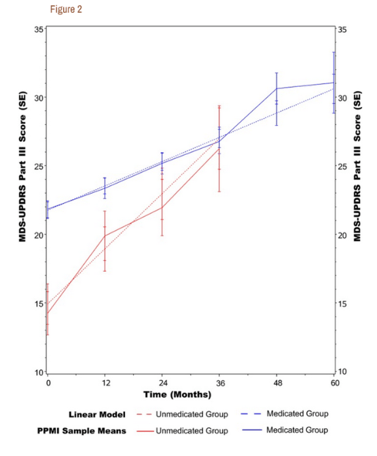
Other studies have reported that Parkinson’s patients’ loss of motoric function is 2.4 points on average per year, and that a 3 point difference should be considered as clinically meaningful.
The results of the Phase 2 placebo-controlled trial
During post market trading hours on December 5, 2022, BioVie has announced that its Phase 2 trial in Parkinson’s disease has met both of its objectives.
Patients treated with the combination of NE3107 and levodopa saw improvements in their UPDRS Part III score that is 3+ points superior to patients treated with levodopa alone.
Phase 2 Parkinson’s study results slide 1 (December 5 Press Release)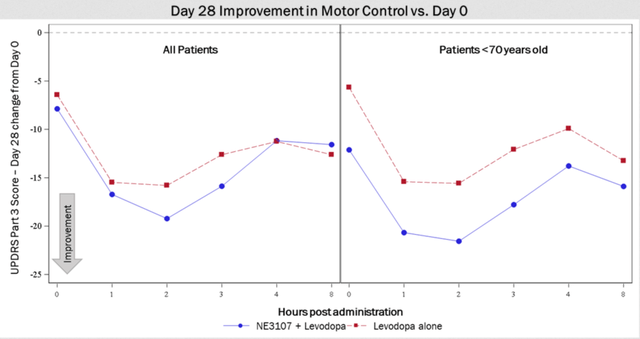
Patients under 70 years of age treated with NE3107/levodopa experienced roughly 6 points superiority compared to those treated with levodopa alone, suggesting that younger patients with less advanced disease progression may experience greater impact from treatment with NE3107. This is consistent with the Phase 2 Alzheimer’s data, and with many other studies, where effects were seen most strongly in patients that had less progressed disease. As a reminder, Parkinson’s sets in when about 80% of the dopamine-producing cells are already gone. Equally, the first brain changes in Alzheimer’s are detected 20 years before symptoms onset.
After 28 days of treatment, 63.6% of patients treated with levodopa alone experienced >30% improvement from Day 0 at the two-hour mark compared to 80% for NE3107+levodopa-treated patients and 88.9% of NE3107+levodopa patients under 70 years old. This pattern is also observed for other time periods.
Phase 2 trial in Parkinson’s – slide 2 (December 5, 2022 Press Release)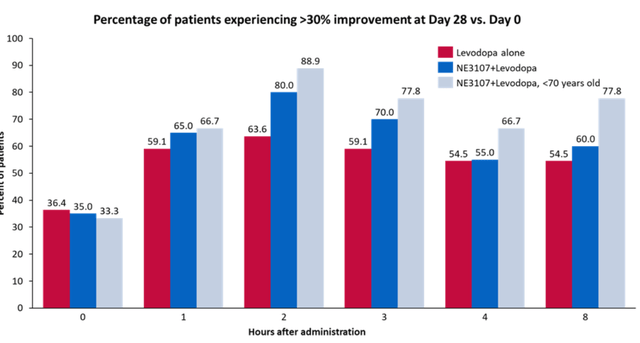
Though these results come from a small study, they are consistent with those seen in Alzheimer’s, as well as with preclinical work. They are credible as well. As an anti-inflammatory insulin-sensitizing drug, NE3107’s effects may very well continue to improve over the course of treatment. For reference, a Phase 2 trial of Exenatide in Parkinson’s disease patients showed a 3.5 point difference on UPDRS Part III, but that effect was only reached after more than a year, in patients in ‘off-state’, who had been off the drug for 12 weeks. Exenatide is – possibly not coincidentally – a diabetes drug, namely a GLP-1 agonist.
NE3107 Seen To Reversing The Biological Clock In Alzheimer’s Patients
In pre-market trading on December 6, 2022, BioVie reported something rather mind-blowing, the more I am looking into it. It had announced that NE3107 appears to have reversed the biological clock of its Alzheimer’s patients on trial by 3.3 years on average after 3 months of treatment.
BioVie had sent patients’ blood samples to Steve Horvath, a world-renowned expert in the field of aging and epigenetics. On the basis of the study of DNA-methylation, Prof. Horvath designs epigenetic biological clocks, which are essentially algorithms designed to find out someone’s biological age. In 2019, a small study combining a growth hormone with two anti-diabetes drugs. Results made world news headlines and were published in Nature, as the study had been able to reverse patients’ biological clocks by 2.5 years over the course of one year of treatment. The study was considered to basically turn back time. Interestingly also, in 2021, a study came out showing that excellent responders to anti-TNF therapy in psoriasis had better SkinBloodAge compared to partial responders.
In 2022, we now have a study that seemingly largely surpasses the above findings of 2019. Treatment with NE3107 for three months showed a reduction of 3.3 years on the Horvath DNA methylation SkinBlood clock. Furthermore, not less than 19 out of the 22 patients experienced a reduction in the SkinBlood clock score.
DNA Methylation Age Skin Blood Clock Slide 1 (December 6, 2022 Press Release)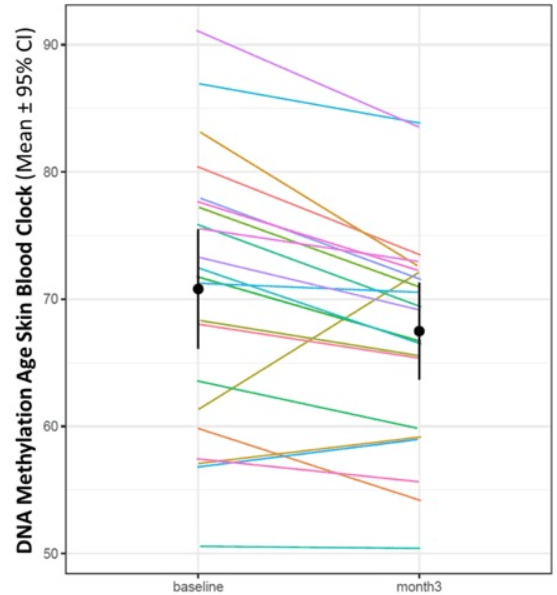
If the Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s data already weren’t, I believe this to be world news. The market may need some time to take in this information, as it comes as a surprise and does not have a frame of reference. Though there are those like Peter Thiel and Jeff Bezos who aspire eternal life, in patients with disease and particularly those suffering from the diseases mentioned above, this finding perfectly underscores the magnitude of potential that NE3107 has.
Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s: market size and treatment landscape
Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease are the two largest neurodegenerative diseases, with no approved treatments available that are able to stabilize or reverse the course of the disease. An estimated 6.2 million people are diagnosed with the disease in the U.S. alone. About 1 in 9 persons aged older than 65 have Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s disease is a growing epidemic as by 2050, this number is predicted to increase to approximately 14 million. The global Alzheimer’s therapeutics market was valued at $ 4 billion in 2021, and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 16 % from 2022 to 2030. I believe this may still be an understatement, given the high pricing we have now seen for the two drugs that have been approved for neurodegenerative diseases, namely Biogen’s Aduhelm at $28,000 per year and Amylyx’s ALS drug Relyvrio at $158,000 per year. And both drugs have been approved on fairly moderate efficacy data.
The current treatment landscape of Alzheimer’s disease in the U.S. consists of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors on the one hand, and Aduhelm on the other hand. Aduhelm was refused approval in Europe, and medicare refuses coverage of anti-amyloid therapies. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors have been approved for decades but only provide temporary relief and do not change the ongoing neurodegeneration. Aduhelm has been approved recently, is barely being prescribed, like the other anti-amyloid therapies comes with a major side effect called ARIA, and may lead to deaths of patients. And its potential successor lecanemab, a drug being developed by Eisai in collaboration with Biogen (BIIB) that recently made headlines for being able to slow down cognition by a moderate 27% – adding billions of dollars to several anti-amyloid players’ market caps – has meanwhile been linked to two patient deaths.
An estimated 1 million people are diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease in the US, with an estimated 10 million people affected by it worldwide. The global Parkinson’s disease therapeutic market’s worth was estimated at $ 4.7 billion in 2021, is projected to reach $ 8 billion by 2030, and is expected to grow with a CAGR of 6.3% until 2028.
The current standard of care for Parkinson’s consists mostly of carbidopa-levodopa, dopamine agonists and monoamine oxidase B inhibitors. Levodopa, still most frequently used, gives patients better control of motor symptoms than dopamine agonists and MAO B inhibitors, but dyskinesias and motor fluctuations develop after long-term use. Dyskinesia, uncontrolled unvoluntary movement of the body, sets in the longer one uses levodopa, and is an effect of treatment, not of the disease itself. Dyskinesia, evidently a very serious additional burden, is the reason why treatment with levodopa is often delayed.
Combined, a good therapy candidate that would be able to be successful in both diseases has the potential to address 7 million patients in the US alone, with $8.5 billion in peak sales potential alone, with global peak sales potential above $13 billion. That would assume the drug is priced at $10,000 per year. I am of the assumption that drug pricing may be considerably higher and still be marketable, perhaps at more than double the pricing, if NE3107 would come anywhere close to stabilizing the disease.
Portfolio Revenue Potential AD and PD (Corporate Presentation)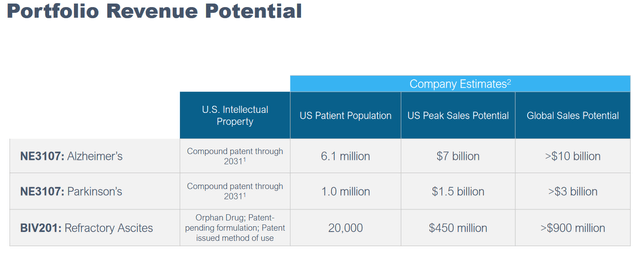
Financials
As mentioned in previous coverage, BioVie could use some additional cash, and it has made it no secret that it may want to raise further cash at a given point. As of September 30, 2022, BioVie had working capital of approximately $17.5 million and cash of approximately $21.2 million. That is a bit higher compared to the quarter before, when it had cash of approximately $18.6 million and working capital of approximately $14.6 million. Its cash burn for 2021 was approximately $27.3 million.
Through December 1, 2022, in accordance with a previous sales agreement that had been filed, BioVie had sold 1,934,871 shares of common stock for total net proceeds of approximately $7.4 million after commissions and expenses.
On December 6, 2022, BioVie has filed further prospectus material allowing it to sell up to $17,500,000 of common stock. I believe that this is also the reason why the share price is under pressure at this time. In fact, BioVie’s stock had gained post the release of the Parkinson’s data as well as after the information on the Alzheimer’s patients biological clocks’ reversal, but then gave away those premarket profits later.
Risks
The risks mentioned in my previous coverage remain largely the same. One of those is that patients may not espond to therapy, as not all Alzheimer’s patients may be helped by BioVie’s anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitizing drug candidate. The non-enrichment of its trials as a function of the biology of its patients is a major difference of BioVie – and pretty much all the other companies involved in the space – to INmune Bio. As explained in my previous coverage, anti-inflammatories seem to have a large potential in about 60% of the entire Alzheimer’s patient population. The question is how they perform in patients whose biology matches the mechanism of action of the study drug less – with less effect, no effect, or an effect to the contrary.
Another risk could be related to the competition. I have mentioned some other competitors above. I do believe that combination therapies are the way forward, and competition should not necessarily exclude the potential for success. A good example is the fact that more than TNF inhibitors has been able to become a commercial success in the past years.
Conclusion
The eventual goal of any therapy in neurodegenerative diseases should be to stabilize or even reverse disease. Eisai’s Lecanemab has probably shown the maximum an anti-amyloid drug can do in Alzheimer’s, namely slowing cognitive decline by 27%, with side effects that are due to brain inflammation.
Anti-inflammatories for neurodegenerative diseases are where the science is at, in view of the abundance of proof that the immune system of the brain essentially goes awry in neurodegenerative diseases. Add to that, an underlying systems dysregulation which is different from person to person, where faulty insulin signaling may be the most common factor.
NE3107 is a drug candidate which appears to be safe, brain-penetrant, non-immunosuppressant, and which targets both inflammation and insulin resistance. In two Phase 2 studies, one of which is placebo-controlled,
Though the Alzheimer’s data undoubtedly addresses a bigger market, the data in Parkinson’s cannot be ignored as there is less competition from treatments like BioVie’s NE3107. BioVie’s readouts validate each other and NE3107’s potential as such.
NE3107 thereby ultimately confirms both the enormous potential of non-immunosuppressant anti-inflammatory agents in neurodegenerative diseases, and its potential to show efficacy in terms of 100% slowing of decline or even better, improvement. To the intelligent investor, this should not come as a surprise anymore. The relevant markets are so humongous that there may also be a place for more than one of these agents. NE3107 is furthest-advanced in Alzheimer’s. A readout of its Phase 3 trial in Alzheimer’s is expected before the end of the third quarter of 2023.
I have set out above why I see a global peak sales potential above $13 billion, at a drug price of $10,000 per year. That cost may come cheap for a truly disease-stabilizing or disease-reversing drug. At a less than $200 million market cap, I believe BioVie’s potential here is huge.


Be the first to comment