Antonio Bordunovi/iStock Editorial via Getty Images
The Nvidia stock (NASDAQ:NVDA) has traded in its strong two-week rally preceding the end of the first quarter for steep losses of more than 20% this month. The stock has underperformed the Philadelphia Semiconductor Index (-11% month-to-date), as well as broad-market benchmark indexes like the tech-heavy Nasdaq 100 (-6% MTD) and S&P 500 (-3% MTD).
Nvidia’s, alongside its industry peers’, latest selloff comes as a result of mounting investor concerns over dampening consumer sentiment ahead of soaring inflation, as well as increasing risks of an economic downturn on the Fed’s aggressive trajectory towards monetary policy tightening. Potential adverse impacts to near-term fundamentals resulting from intensifying Russia-Ukraine conflicts and ensuing sanctions that were previously downplayed are now also becoming more pronounced. Worries heightened over added pressure on already-fragile supply chains and effects on industry sales after Russian President Putin vowed to continue its “military operation”, citing peace talks with Ukraine have now reached a “dead end”.
Yet, from company-specific and longer-term perspective, Nvidia’s financial outlook remains robust, thanks to its continued prowess and market leadership in graphics cards and artificial intelligence. As discussed in our previous commentary on Nvidia’s latest GTC presentation, the chipmaker’s continued commitment to innovation will only further its growth opportunities over the longer term, while also bolstering its competitive leadership ahead of a bullish chip demand environment.
The near-term macroeconomic challenges may be fuelling the paradox in Nvidia’s near-term stock price movement, but its fundamental strength and outperformance are expected to prevail and regain investors’ confidence over the longer term.
Brewing Macroeconomic Implications on the Semiconductor Industry
Hot off the press Tuesday was the U.S.’ March inflation print. The number hit a fresh 40-year peak at 8.5% due to soaring commodity costs on protracted COVID and war disruptions on supply chains, fanning market fears over a multitude of macroeconomic challenges ahead. Investors were already spooked by a series of hawkish comments from Fed officials and aggressive monetary policy tightening plans outlined in the FOMC March meeting minutes released earlier this month, leading to the stock market declines observed over the past two weeks. And with the latest CPI data coming in at another generational all-time high, markets are bracing for the “fastest monetary tightening since 1994”, which combines a half percentage point rate hike at the upcoming FOMC May meeting and an aggressive rundown of the Fed balance sheet beginning as soon as June.
Both policy tightening tools aimed at quelling inflation at all costs certainly do not bode well with risk assets – especially high valuation growth stocks like Nvidia. On one hand, rising interest rates spell higher costs of borrowing, making it more expensive for a sector that is focused on investing in long-horizon growth. Although Nvidia’s strong balance sheet (low leverage, high operational cash inflow) provides insulation on this front, aggressive rate hikes ahead still risk eroding the present value of its future earnings.
Meanwhile, on the other hand, an aggressive rundown of the Fed’s balance sheet, which is currently capped at $1 trillion per year based on the March meeting minutes released, also fuels the risk-off environment in equities. U.S. Treasury yields have already been surging on an extended sell-off and briefly surpassed 2.8% earlier this week for the first time since March 2019. The benchmark inflation-adjusted yield is now nearing positive territory, meaning benchmark Treasury yield is close to surpassing inflation for the first time in two years. The trend, combined with rising interest rates’ threat on valuations, have together encouraged a further rotation away from growth stocks, which represent the “riskiest corners of the market” and are largely categorized as “economically sensitive”. This is further corroborated by losses observed in the tech-heavy Nasdaq 100, which has lost more than $1 trillion of its market value over the past week.
Near-Term Fundamental Implications for Nvidia
Given the macroeconomic headwinds outlined above, investors are diverting focus from the March CPI data to the upcoming earnings season as they “evaluate the threat from inflation, amid concerns that rising commodity costs and more circumspect consumers will end up squeezing company profits”. But speculations on near-term fundamental adversities over the semiconductor industry are rising, further weighing on the industry’s market performance in the past two weeks.
Recent analyst findings are warning of an “unexpected decline in chip orders” and a handful of “order cancellations related to excess inventories” observed in early April, which could imply a near-term demand slowdown stemming from reasons such as temporary production halts and delays due to widespread COVID restrictions in China, as well as reduced sales due to sanctions imposed against Russia’s assault on Ukraine. The bigger market worry is that consumer electronic OEMs are now cutting back on chip orders due to a structural downturn resulting from rising inventory stockpiles amassed during the worst of supply chain constraints. However, the scenario remains unlikely, considering demand for semiconductors remains higher than ever before, as evidenced by record sales reported by TSMC (TSM) and Analog Devices (ADI).
Accumulating macro and fundamental fears have driven declines of more than 7% in the Philadelphia Semiconductor Index over the past week, marking one of the industry’s worst sell-offs since January. Yet, global chip sales have increased by more than 30% year-on-year in February, marking the “11th consecutive month of growth above 20%”. With chips being an enabler of everyday essentials ranging from computers to cars to data center equipment, consensus estimates for sales and earnings growth in the current year are averaging 17% and 18%, respectively, up by more than four percentage points from prior year expectations and almost double of the average sales and earnings growth forecast for the S&P 500. Even in the face of runaway inflation and aggressive tightening of central bank policies that risk pushing the economy into a recession, the demand environment for semiconductors – especially the full-stack, hardware-software offerings by Nvidia, which are critical to enabling digitization trends in the post-pandemic era – is unlikely to see any structural, massive contraction. The global chip supply shortage also remains prominent, especially with added pressure from impacted productions due to the recent outbreak of COVID infections across China. This will continue to buoy Nvidia’s pricing power, and inadvertently, top-line growth, as downstream OEMs like automakers continue to look for ways to mitigate lost sales that topped $210 billion over the past year.
Despite speculations of some potential near-term slowdown, Nvidia’s outlook on outperforming the broader semiconductor industry’s average sales growth in the current period remains promising. And this will likely be the key determinant for the stock’s rebound, as growth resilience is expected to restore investors’ confidence amidst mounting macro challenges. Our base case forecast expects total revenues for the fiscal first quarter ending April to increase by 43% year-on-year to $8.1 billion, which is largely consistent with management’s issued guidance. And for the full fiscal 2023, total revenues are projected to increase 37% from the prior year to $36.8 billion.
Nvidia FY/2023 Revenue Projection (Author) Nvidia Long-Term Revenue Projections (Author)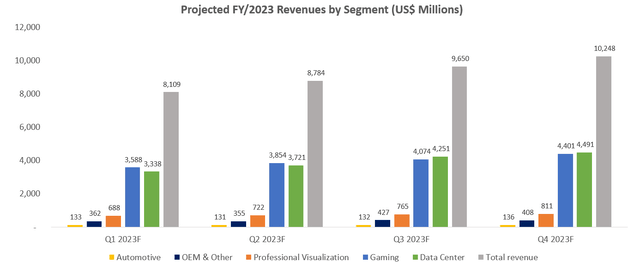
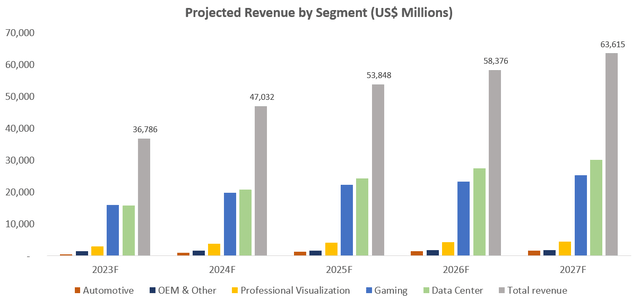
The forecast accounts for softer gaming revenue growth compared to the prior year, considering a potential slowdown in near-term discretionary consumer spending due to rising prices and nominal impact from the sanctioned Russian market. Over the longer term, Nvidia’s continued commitment to innovation, as discussed in our previous coverage, will play a critical role in beating out competition and maintaining its market leadership in gaming. For instance, the newly launched “NVIDIA H100” GPU based on the newest “Hopper” architecture is expected to be “the world’s largest and most powerful accelerator” for high-performance computing (“HPC”). According to Nvidia, “twenty H100 GPUs can sustain the equivalent of the entire world’s internet traffic”, underscoring its continued prowess over next-generation computing and advantage over new offerings by industry peers, like the Intel Arc GPU (INTC).
Professional visualization segment revenues are expected to remain strong in the first half of the fiscal year on early-stage Omniverse-related sales, with continued ramp-up in adoption buoyed by new feature roll-outs and broadened application use cases. Meanwhile, automotive segment sales will remain impacted in the first half of the fiscal year due to worsening supply chain bottlenecks from the recent COVID resurgence in China and ongoing war in Ukraine, which have constrained auto production output in the current year. But over the longer term, Nvidia’s full-stack autonomous driving solution offerings (“NVIDIA DRIVE“) will benefit from continued development and rapid adoption of self-driving technology.
Nvidia Financial Forecast (Author)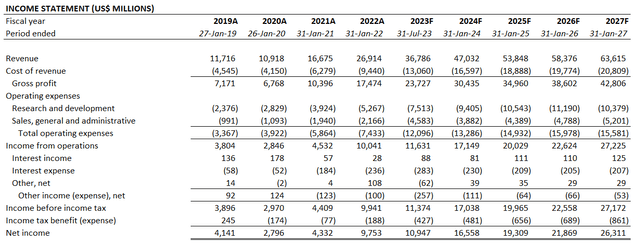
The Impact of Doubling Nvidia’s Authorized Share Count
Aside from market-related headwinds, the latest company-specific challenge to the Nvidia stock’s performance is the company’s request for shareholder approval on doubling its current authorized share count. Nvidia outlined in its most recent Form PRE 14A filing to the SEC on April 8th that it is “seeking approval of an amendment to [the] Restated Certificate of Incorporation to increase the number of authorized shares of common stock from 4 billion to 8 billion shares” at the upcoming Annual Meeting of Stockholders in June.
Unlike mega-cap peer Tesla’s (TSLA) recent proposal to shareholders for a share count increase to facilitate a potential stock split in the near term, Nvidia has only provided a generic statement on the matter, citing the proposed share count amendment would enable the issuance of shares for “general corporate purpose, including, but not limited to, stock dividends and/or stock splits, expanding [the] business through mergers and acquisitions, providing equity incentives to employees, officers or directors, and the raising of additional capital”.
The announcement pushed the stock 4% lower right out of the gate during Monday’s (April 11th) regular session, underscoring investors’ fear for potential share dilution in the latter half of the year. But considering Nvidia’s consistent growth track record and strong balance sheet, it is not one to act against shareholders’ interests. The proposed share count increase is likely resulting from the need for greater flexibility in raising capital to fund the company’s longer-term investments, especially considering Nvidia’s expanding innovative technology pipeline, which facilitates further capitalization on growth opportunities ahead. This is also consistent with the proposed funding structure on the previous Arm deal that had fallen through, which consisted of $21.5 billion in Nvidia common stock and $12 billion in cash. Equity funding complements the company’s currently robust balance sheet as well, while also providing partial insulation from rising debt costs as a result of proposed rate hikes by the Federal Reserve over the next two years as discussed in earlier sections.
The other case is that the proposed increase to Nvidia’s current authorized share count will be used to facilitate a potential stock split in the future, a favourable strategy that has regained popularity in recent months. While stock splits do not change a company’s fundamentals, the strategy has historically dawned a rally for Nvidia, thanks to increased demand from retail investors who enjoy the ownership of whole shares but are averse to high prices. Considering Nvidia’s accelerated business expansion and subsequent surge in valuation since its last stock split in 2021, a similar strategy could be in the works to attract greater market participation in the company’s long-term growth prospects.
Valuation Sensitivity Analysis
Nvidia’s valuation premium to its semiconductor peers have largely diminished following the extended rout through April. Based on industry-wide valuation multiple contractions observed over the past several months in response to the current shaky macroeconomic climate, Nvidia’s last traded share price in the $210s zone on April 12th tracks well on par with its peers. Based on the semiconductor peer group’s forward implied growth-valuation correlation plotted below, applying Nvidia’s projected 38% sales growth for the current year, as discussed in earlier sections, would yield an exit multiple of about 24x.
Semiconductor Industry Peer Comp (Author)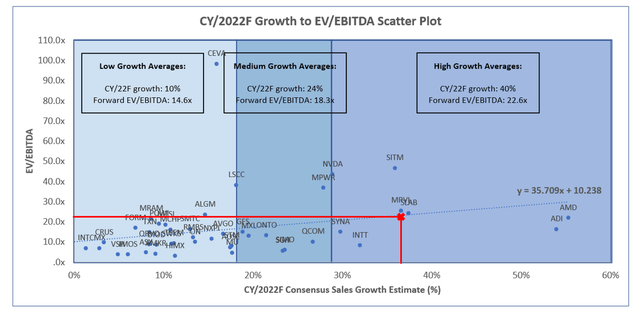
Applying the 24x exit multiple alongside a 12.1% WACC determined based on Nvidia’s current risk profile and capital structure to our discounted cash flow valuation analysis would result in a valuation of about $212 on a per-share basis.
Nvidia Valuation Analysis (Author)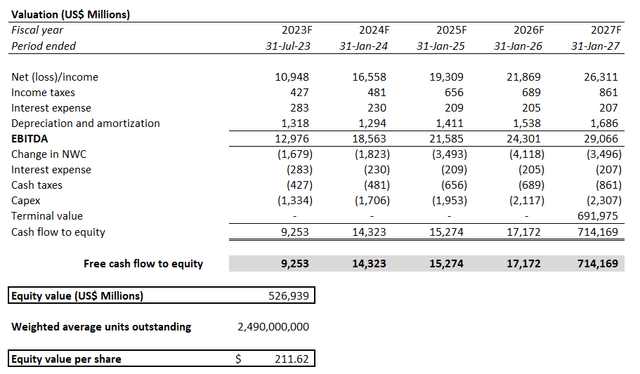
However, considering Nvidia’s historical valuation premium to peers, which is in our view reasonable given its market leadership (more than 80% GPU/AI processor market share) by wide margins against comparable peers, the stock will likely rebound to trade higher on proven growth resilience in the upcoming earnings season and once the market storm clears.
Nvidia Valuation Sensitivity Analysis (Author)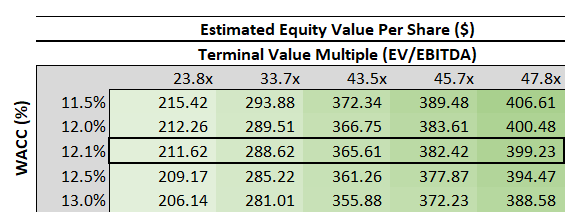
Conclusion
Considering the structural importance of Nvidia’s role in enabling core digitization trends in the coming decade, the company’s demand environment remains one of the strongest in the industry despite the near-term macro challenges. While we are expecting further volatility leading up to the Fed’s policy decision on rate hikes and its balance sheet reduction coming May, amongst other unresolved matters like extended COVID and war disruptions on already-fragile supply chains, the Nvidia stock remains on a positive track towards delivering a strong showing over the longer term.
Author’s Note: Thank you for reading my analysis. Please note that we will be launching a Livy Investment Research Marketplace service on March 31st. The service will allow you to follow my coverage portfolio, interact with me directly, and participate in chat rooms with other subscribers. Early subscribers will receive a legacy discount at $249 per year. Stay tuned for more details as we ramp up to launch in the coming months.


Be the first to comment