Douglas Rissing
Well, the Federal Reserve posted another 75 basis point rise in its policy rate of interest. The range now for the Federal Funds rate is 3.75% to 4.00%.
Another rate increase is expected to take place at the next meeting of the Fed’s Federal Open Market Committee meeting in December.
The Fed’s securities portfolio declined by $33.8 billion in the last banking week, the one ending November 2, 2022, bringing the total decline in the portfolio since March 16, 2022, to $234.7 billion.
And, the Fed continues to talk tough about sustaining its “tightness” program.
Reserve Balances with Federal Reserve Banks, the line item in the Fed’s weekly H.4.1 statistical release that represents a measure of commercial bank excess reserves, dropped by $61.1 billion in the latest banking week.
That is, the reduction in these reserve balances support the higher range of the Fed’s policy rate of interest.
Since March 16, 2022, when the Fed began its “tightening” effort, reserve balances have dropped by $846.4 billion as the Fed has raised its policy rate of interest six times.
Here is the picture of the Fed’s efforts to tighten up the reserve position of the commercial banking system.
Reserve Balances with Federal Reserve Banks (Federal Reserve)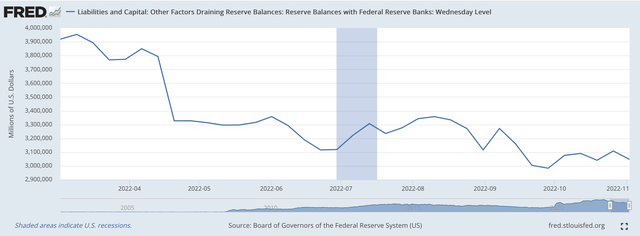
Thus, the Federal Reserve raises its policy rate of interest, the Federal Funds rate, but supports the increases in the policy rate of interest by reducing the amount of liquidity that exists within the banking system.
Method
The Federal Reserve has reduced the amount of liquidity in the commercial banking system in two ways.
First, the Fed has allowed securities to mature from its balance sheet and not replace them so as to reduce the overall size of the securities portfolio.
As mentioned above, the securities portfolio has declined by $234.7 billion since March 16, 2022. We need to report that the “net” unamortized premiums on the Fed’s balance sheet have also declined during this time period by $32.3 billion.
Bringing these unamortized items into the picture raises the decline in the value of securities on the Fed’s balance sheet to $267.0 billion.
Second, the amount of Reverse Repurchase Agreements have also risen during this time period.
Reverse Repurchase Agreements are a liability item and represent the sale of securities to dealers under an agreement to repurchase the securities after a very short period of time.
In the latest banking week, reverse repurchase agreements rose by $91.2 billion. Since March 16, reverse repurchase agreements have risen by $716.0 billion.
Reverse Repurchase Agreements (Federal Reserve)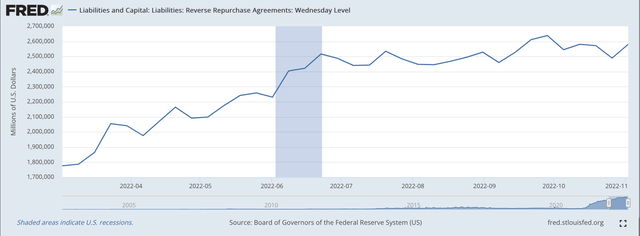
Note, then, that these two items have contributed to a $983.0 billion decline in Bank Reserves with Federal Reserve Banks since March 16, 2022.
Some of this reduction has been offset by outflows of government monies held U.S. Treasury accounts at the Fed, which drops the $983.0 decline back down to the $846.4 reduction in the Reserve Balances with Federal Reserve Banks.
So, to manage the tightening up of funds in the banking system to support the rise in the Fed’s policy rate of interest, the Fed uses several different accounts on its balance sheet.
Summary
While it is important to closely watch what the Federal Reserve is doing with respect to interest rates, it is also very important to watch what the Federal reserve is doing with its balance sheet.
The Federal Reserve has pumped a lot of liquidity into the financial system since the early stages of the Covid-19 pandemic.
This liquidity has resulted in major increases in the M2 money stock. These increases in the M2 money stock are having a major impact on inflation, the very variable the Federal Reserve is trying to reduce.
In 2020, the M2 money stock rose by just under 25.0 percent from December 2019 to December 2020.
From December 2020 to December 2021, the M2 money stock rose by 12.5 percent.
This rate of increase has only dropped by 4.1 percent if we look at the August 2021 to August 2022 data.
So, if one looks at the monetary data up to this point, the Federal Reserve seems to be having an impact upon the rate of growth of the money stock, but, it appears as if the Fed has a long way to go to get the inflation rate anywhere close to its 2.0 percent target.
M2 Money Stock (Federal Reserve)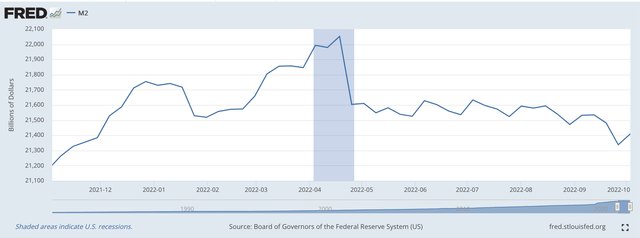
That is why, to me, it is more important to watch what the Federal Reserve is doing to its balance sheet and how these moves are impacting financial variables like the M2 money stock. Just watching the movements in the Fed’s policy rate of interest is not enough.


Be the first to comment